This post is also available in: 日本語 (Japanese)
In 2017, Unit 42 reported on and analyzed a low-volume malware family called Cardinal RAT. This malware family had remained undetected for over two years and was delivered via a unique downloader named Carp Downloader. Since that publication, we have continued to monitor this threat, resulting in the discovery of a series of attacks using an updated version of Cardinal RAT. A series of modifications have been made to the RAT, many of which are used to evade detection and hinder analysis.
We witnessed attacks targeting the financial technology (FinTech) sector, primarily focused on organizations based in Israel. While researching these attacks, we discovered a possible relationship between Cardinal RAT and another malware family named EVILNUM. EVILNUM is a JavaScript-based malware family that is used in attacks against similar organizations.
Cardinal RAT Employs BMP Trick
Since the original discovery of Cardinal RAT, the attackers have made some minor updates that are worth discussing, particularly regarding obfuscation techniques. For the sake of this analysis we’ll look at the most recent version of Cardinal RAT:
| SHA256 | b742162197744a8caeb09f954213a3172ed699f8375f69c40b57b8c219c5e37c |
The last time we wrote about Cardinal RAT in 2017, we looked at version 1.4 of the malware family. We identify this latest sample as version 1.7.2 based on information within the payload. Unlike previously discussed samples, this latest instance of Cardinal RAT employs various obfuscation techniques to hinder analysis of the underlying code. The first layer of obfuscation comes in the form of steganography; the initial sample is compiled with .NET and contains an embedded bitmap (BMP) file.
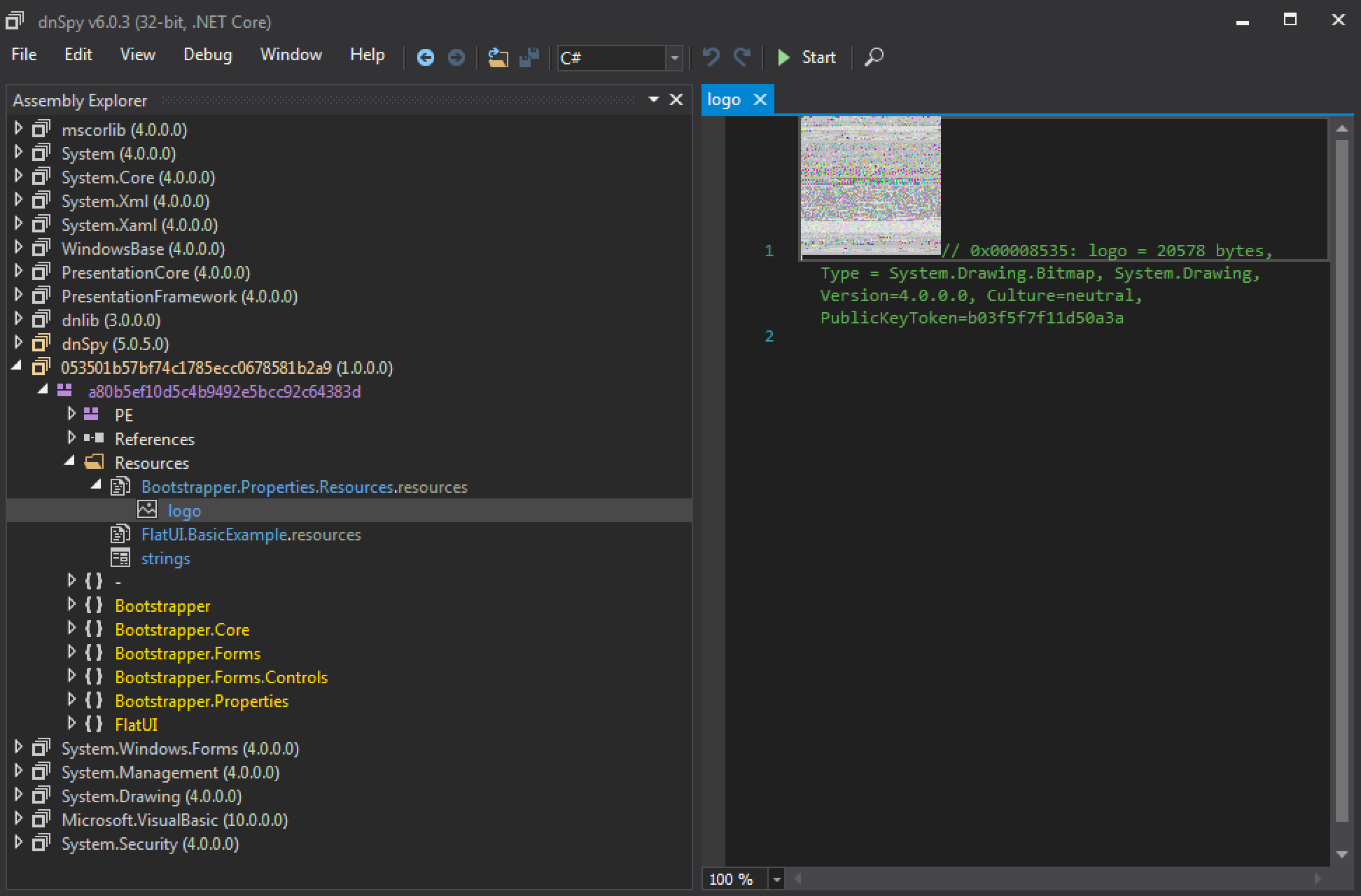 Figure 1. Embedded BMP file contained within .NET loader
Figure 1. Embedded BMP file contained within .NET loader
Upon execution, the malware will read this file, parse out pixel data from the image, and decrypt the result using a single-byte XOR key. We have provided a Python script to automate this process in the Appendix of the blog post. The result is a DLL also compiled with .NET, with the following hash:
| SHA256 | 01e007b8304eb0cbcb2be11ddb86298dc85c084fb5459eda319a69ef50799f88 |
After this file has been loaded in memory, the initial loader will load and execute the ‘corerun’ function, initiating the second stage of the malware. The DLL begins by performing a sleep using the built-in Windows choice utility:
cmd.exe /c choice /C Y /N /D Y /T 20
The command prompts the user for a choice with a 20 second timeout, at which point the process will exit. Since the window is hidden, and there is no utility for this choice, the malware simply uses this as an alternative sleep command.
The second stage DLL reads in the ‘strings’ embedded resource from the first stage executable. Part of this resource is decrypted to provide configuration information to the dropper. This configuration information will instruct whether or not the malware enters its installation routine. In the installation routine, it begins by writing a unique GUID identifier to %TEMP%\[random].ini. Afterwards, it creates the following directory:
%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\IEConfig
It then writes an embedded executable with the hash below to %TEMP%\[random].exe. This file has an internal filename of RunExecutive.exe and simply copies the contents of argument #2 to the file path specified in argument #1.
| SHA256 | 2167d393ec89ec0c6e2d7557a7ad22aa1953dd8082f599bee14977c25a128cce |
The malware creates an LNK file in the victim’s startup folder with a randomly generated filename using a GUID (Example: {fcb29182-b3cc-47e2-a95c-b22c6d87dda1}.lnk). The LNK file executes the following command:
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -windowstyle hidden "%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\IEConfig\[random]\sqlreader.exe"
Finally, the malware will execute the previously written RunExecutive executable with arguments to copy the original executable to the previously referenced sqlreader.exe file path.
The remaining segment of the embedded resource is decrypted using a 16-byte XOR key, resulting in a .NET executable. This executable is injected into one of the following two legitimate executables or processes on the system:
- RegSvcs.exe
- RegAsm.exe
In previous versions of this malware family, there were a larger number of legitimate processes Cardinal RAT would inject into. The final payload has the following hash:
| SHA256 | 04de4b51c881e65236c9efdbfbc0099e6b48fd1723a6e51bf480b52104dd2ba2 |
Underneath all this obfuscation, this Cardinal RAT payload does not have any significant changes compared to the previously discussed version in terms of its operation or capabilities. One of the most significant changes lies in the obfuscation used by the malware; all of the functions, methods, and variables have been renamed to MD5 hashes.
Figure 2. Obfuscation present in Cardinal RAT payload
In addition to the obfuscation routines in use, there have been a few minor changes within the malware itself. First, the embedded configuration has a few changes both in the order of the embedded values, as well as what values are present. Additionally, the way this configuration is encoded has changed slightly, as several values that were previously base 64 encoded in version 1.4 are no longer base64-encoded.
$ python parseConfig.py GreyCardinalConfig
Mutex: {509ce3ef-e03e-467e-be19-710782f13c28}
Campaign Identifier: '\xf1\xaf\x02i.]\xa4\xe0'
C2 Server: affiliatecollective[.]club
C2 Port: 443
Hash Value: 0304674e9876530dfbea5a9b4fec7b98
Additional C2 Servers: 0
GUID: '\xd6\x04hr\x9a\xedLN\xae\xe8\xd0\x87\x80\x19\x15z'
Buffer Size: 81920
Max Buffer Size: 40960000
Sleep Timer Between Requests: 2000
Unused Integer: 60000
Unused Integer: 0
Perform Keylogging: 0
Disable Sleep on Victim: 0
Network communication and actions available to the remote operator remain consistent between versions. The script provided in our previous report continues to work as expected against the network traffic generated by this malware family. The following actions continue to be present within the malware:
- Collect victim information
- Update settings
- Act as a reverse proxy
- Execute command
- Uninstall itself
- Recover passwords
- Download and Execute new files
- Keylogging
- Capture screenshots
- Update Cardinal RAT
- Clean cookies from browsers
Enter EVILNUM
When looking at files submitted by the same customer in a similar timeframe to the Cardinal RAT samples, we saw that the customer had also submitted a malware family we’d been tracking as EVILNUM. From our viewpoint this is another family that seems to be used solely in attacks against finance related organisations.
When we cross-referenced submissions to online sandboxes, we found an additional case to ours, where another organization had submitted both EVILNUM and Cardinal RAT on the same day; both of which are rare malware families with limited distribution.
We opted to use the name EVILNUM, since in some versions of the malware the C2 is calculated by reading the page, parsing a numerical value, dividing it by 666 and then converting the resulting decimal to an IP address. There are at least two versions of this malware, one written in JavaScript, and another written in .NET.
| SHA256 | Type |
| bee6c5a506d6fb2cc129443c74b7676fbb9a79b53b92b2cac4c7fb8209592714 | .NET |
| 97c97ad2baef37eea023549131c192f441aa7976747166cd31095e7dad17948c | JS |
Despite the differences in programming language used, the samples are similar, and we believe the .NET edition is likely a rewrite of the .JS version.
EVILNUM has been covered in the public domain previously (albeit with no name assigned to the malware family) and has been noticed by multiple analysts on Twitter. It’s a first-stage malware family which gives an attacker data about the infected host before they decide to install other utilities on the machine. EVILNUM’s supported commands vary from version to version and include but are not limited to:
- Setting up persistence
- Run an arbitrary command using “cmd /c”
- Download of additional files
- Ability to take screenshots
Since the operation of the malware is well covered already in the pwncode article, we’ll simply illustrate a few of the differences and similarities between the older and newer versions of the malware in the table below:
| May 2018 version | January 2019 version | |
| Version # | 1.3 | 2.1 |
| C2s used | Public Forums/Git, find number, divide by 666, num2ip | Public Forums/Git, find number, divide by 8, num2ip |
| Functionality to steal local cookies | n | y |
| Use of Lock file | y | y |
| Adds to Startup as LNK? | y | y |
| Add to startup method? | via cmd line | By importing a reg file |
| Function naming | this_function | ThisFunction |
| Ability to take screenshots | n | y |
Table 1. Highlights of the similarities (in green) and differences (in red) between EVILNUM versions
The malware appears to have been given a general rewrite, (as indicated by the authors’ version number) with many functions being rewritten from scratch.
Despite this, the core functionality of the malware is mostly the same, and some of the concepts used in the malware family (such as the lock file) remain the same. It’s likely that the malware only serves as a first stage and the attackers deploy further tools to target networks of interest.
Targeting
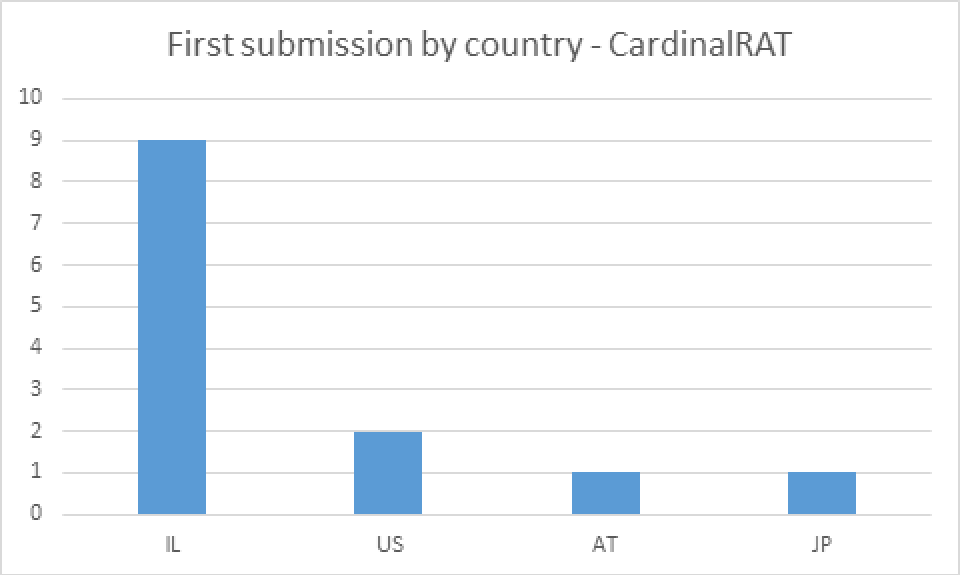
Since April 2017, we have observed Cardinal RAT in attacks against two customers, both customers were FinTech companies who write software relating to forex and cryptocurrency trading, and both companies were based in Israel. Looking at submissions to VirusTotal, there are 13 Carp Downloader documents. Note that we are only looking at submissions for “entry” type files, not subsequent dropped files. When looking at the first submitters for these documents in Figure 1, we see they are predominantly uploaded from Israel.
Figure 3. Distribution by country for Carp Downloader submissions to VirusTotal
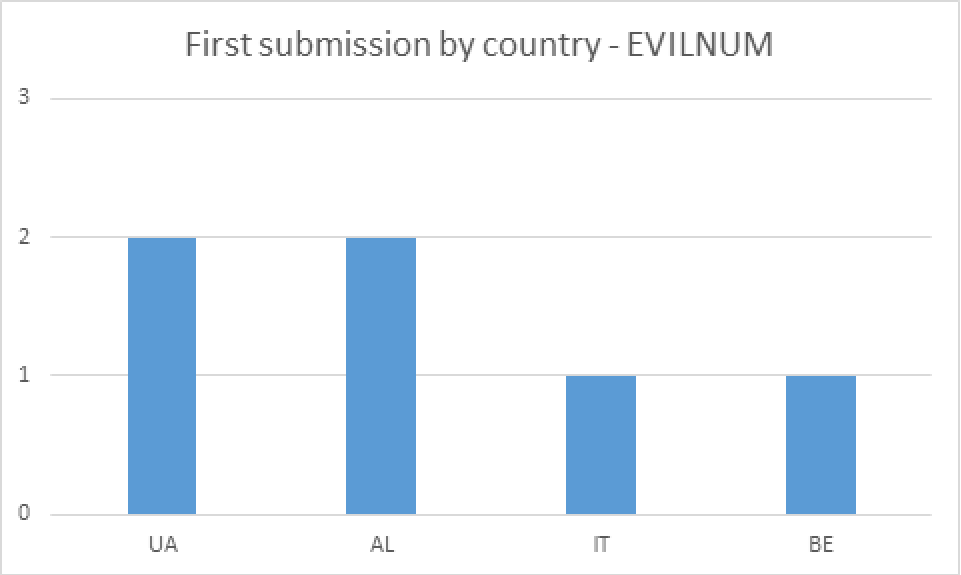
In the case of EVILNUM, we have only seen one instance at a customer (the same one we referred to earlier in this article). When it comes to investigations from public sandboxes though, the distribution of the initial files used in infections is most commonly via LNK files. The geographical distribution of first submitters for EVILNUM is quite different, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Distribution by country for EVILNUM submissions to VirusTotal
Conclusion
Cardinal RAT and EVILNUM are both used in limited distribution attacks against FinTech companies. In one case, both families were observed at the same target in a short space of time, whilst droppers for both families share similarly themed lure documents.
We suggest that these families are used in targeted attacks against FinTech companies because:
- Our telemetry shows these families are only used against companies in this sector.
- The lure documents used consistently related to lists of names/numbers of individuals involved in trading forex/crypto currency, a niche theme to use if targeting individuals outside of this sector.
We believe it’s possible that both families are used by the same attackers because:
- We know of two cases where a company was targeted or appears to have been targeted by both malware families in short succession.
- Both families have been distributed using malicious documents containing lists of names/numbers of individuals involved in trading forex/crypto currency.
- The differences in geographical distribution can be easily explained as a difference in visibility.
However, there are a number of arguments against the two families being related:
- In terms of the geographic spread of where these families are seen, the targeting for each family seems to be quite different.
- The delivery methods for each family do not share any similarities.
- The infrastructure associated with each malware family is distinctive and different with no cross-over in terms of hosting providers or other attributes being observed.
Even if the two families are not linked, they both have similar targeting interests, and so FinTech organisations should ensure they are protected against the malware used. Whilst we haven’t been able to gain an insight into what the attackers do once successfully on a target network, it’s likely (based on the targets) they use their access to facilitate financial gain.
Organizations with effective spam filtering, proper system administration, and up-to-date Windows hosts have a much lower risk of infection. Generic defenses against these threats include:
- Do not allow inbound e-mails with LNK file as attachments, or, do not allow inbound e-mails with attached ZIP files containing a single LNK file inside them.
- Do not allow inbound e-mails from external sources where the documents contain macros, or, if you do, ensure proper policy is configured.
- Enforce parent-child process policies to restrict use of scripting languages by malware.
Palo Alto Networks customers are further protected from this threat by:
- EVILNUM variants are blocked by our IPS, see threat IDs 18781 and 18782.
- Wildfire and Traps detect all files referenced as malware.
AutoFocus users can track this activity using the CardinalRAT, CarpDownloader and EVILNUM tags.
Appendix
Script to decrypt BMP from Cardinal RAT dropper
from PIL import Image
import sys
from struct import *
im = Image.open(sys.argv[1])
pix = im.load()
width, height = im.size
fileSize = unpack("I", (pack("bbbb", pix[0,0][0],pix[0,0][1],pix[0,0][2],pix[1,0][0])))[0]
key = 187
out = ""
for ind, h in enumerate(range(height)):
if ind == 0:
j = 2
for w in range(width-2):
pixel = pix[j, ind]
out += chr(pixel[0] ^ key)
out += chr(pixel[1] ^ key)
out += chr(pixel[2] ^ key)
j += 1
else:
for k in range(width):
pixel = pix[k, ind]
out += chr(pixel[0] ^ key)
out += chr(pixel[1] ^ key)
out += chr(pixel[2] ^ key)
finished = out[0:fileSize]
print("Writing output to 'dumped.exe_'...")
fh = open("dumped.exe_", 'wb')
fh.write(finished)
fh.close()
Indicators of Compromise
Cardinal RAT samples
b742162197744a8caeb09f954213a3172ed699f8375f69c40b57b8c219c5e37c
06151c14153e983ae7ab793c7cd0e5ac3faf8e200894955b02e1191429eff29a
9e6671a8af28e0ab6c37c044d85a2406b665a171ae3bef46f3e90d06e33027ae
448c33094322b200c53ff016fec29469b3e52def359430113115cc70d7f28704
06f1348c8a2ffab67627556075ddcad92998526d4d3802b9c2357d169531825f
ca8af85f7eed79a73984b2dccd3dd2148865dfed7a009842be7372e6ce18037f
75ca794f265ebad84954f13480e0e31c17048d21c4b52e949864c951437d0c2c
78e2929e5dae8677f9db3aa7eaa96ad584c872343698e18f85349a027328b3ea
f4f52c45ca3d4d4ce33981f660d23e8df4a9c0e345fdd6429d8b46f6c0528c38
dd8fe0e27bf798cace40ac0d58b833ba3bbf16d80175296601585ed1964465ec
20fec2d1824b585aa558b7cf9e9980acd665736ce9f7a124507cf46afb30c79f
dab228c236d48fa1660bcec59e17e5004726741a85b0fbeef8300f29927c32d9
f75883ff35104a032dd047ca39d35ec98601c76aa02f58ad655df6deaadecb55
a545288c4d491d510972d583b773f8a0c5dc355942e322cf767d33121c659c1c
64a9bdf4ff33e8f2e74dc16d7dce0f392aa130ff9b99458778fd25d9aadff381
66f38591e8c80bb26623b0e6be5ab976fdf745c2afa020c7d98e2814960b5961
65b726aab53920c497f83eb1f3cbd6b7dbfc2074aab6761b7485aa98f2df139a
3ec85a019a480114856d3022961d7a55c1ae7cfa81b0073b2c1abcf99e0e541f
43fb0b13f9872a54f91a7bf202b23a8a16de99d054a83ed08b9ea97f9e2675e8
137f9265cba1101ae5d63b94c6ad1b47c7d02f0ab4f54a1af3169422791790cf
101af6fdb990e5e9584382a65f5cee7efd9e89c38e928beca18419bdf70ef076
f9bccd349cf841d0f25e81d80a1b4bf73dd960a1f3aa71029a18e36480c80392
f027735c3db77e67cf7bada8862ddbb0d85a2caacbb4b2825e4acdfa863a14c9
75996bbfcd2b343523ed79476f9516cc7d2b041c43841e5e735db4f22ae970c3
0097dd7676b810bd0c1c70d8c86604c830e1e8e88f6a13c3869747faba381076
08ce077e8d54db08ede1095d03286146d04e8cbce74ec91a9fc7b9d0a99ddb9f
28e9e0fcc6899db7a16315d3dca38b6166ba318f8ca07b422ebadaab209b589b
2247c528fc1b90b725d857cc5d45572e864c6c4948100458774f0ef6a8f11403
dfa041f6cbe9d83cdaaed90466693efca33729c99fa43b29ab8e44bb27eb0a6b
4045950ffa263b92774e92ab36b3ec52bf18f1c133b8d155819629d2ad4b3d1c
85f1053041ef7af8a1c3d941e18de21e7adc24537863063d127bab8a8d2dc64b
98200955db80cb5835158320ba94b2b55bc7028ea988b75f02adee3df40793f3
ae8fb2f138981f10092761768428fb312e3e49bc23d5b610e3127c1a387aede8
66f43e57648f01ea5f8d0d152db1df90c764eebeb701403936a15c47e2965353
943cef39e54457fcfa21f5a8ed0f04095c1d4b798453770be5dda5db7d5406ac
ca2a01792873233693e17fe51c4c86c05d07e31f9b579ab0444dd89733633532
4fde64e9391d36aaff700ce0be3df9e7e6303b6de114332286de694af33dd7da
5909b5999d3998f578a3acb4bf85e0b3fde102c417c40b6beed0dd3b8ceb51bf
0212334200668ac64cb63fc1a4f4ea17e956f6928a2211c945c2e07f1b25a3ef
bae230d6a988723b33158bbeef4ab90b1bff7b521fed9cab0c5e1f5b69a01de5
b01b7a5798f41a5fae54b4189db6f47c6110a0b53a4df32cb7d0f13503c5250c
fb63acfda1730132dbfbf1d46834d771156aac3f7c8e97ea136ca6edbe811fad
268c3c9a98f2a15aaab9b0488225b0ba4e3d35efa30f6fed9052ffd31042bd7b
0afec067628e901f7151861b0924ffb1909d21a707177b1e6cf2c8d491bb1a60
985d893426373d4e71386d731e5bc44c1c2ac93e0920dddeb4380929af43dfcb
82017e34c232e05094c2bbed2e62f6b55c1ed8f645803784cac791cc4690beaf
8d8ccaf5a241112d173147b6b08ad5b7953c940ff5928e3046781c1e58a9c73a
427b635915e0fe313ce58175faa1cc240ae26183fb88d05864bc20ef6d87aca3
00f93492edb3274f71686fa469f6c9031a94292a2776c623a1596f710bf4eaa1
5dcec8a061195bd4a2c3e96afecc48b1f0143b6ac4644c518ed8a923d2dcbe21
02e85f39adf8613fd1be610e4e76f4fac08949f2e0198e8cf89a7c3a17cdd6d9
5e60f17396e2ddfce8e60c964056d63cc3b17646c31b4a4f934c2d1fb4f5ba71
cbcb627ff2220ed269aaa58203e7e89f1988210073d35f5f4019f8ecfd012f81
267b1df7bc64c1b93b604d964f52801733fdd43efaf7742810b9277f00ad17ff
e017651dd9e9419a7f1714f8f2cdc3d8e75aebbe6d3cfbb2de3f042f39aec3bd
778090182a10fde1b4c1571d1e853e123f6ab1682e17dabe2e83468b518c01df
8fababb509ad8230e4d6fa1e6403602a97e60dc8ef517016f86195143cf50f4e
1977cedcfb8726dea5e915b47e1479256674551bc0fe0b55ddd3fa3b15eb82b2
16aab89d74c1eaaf1e94028c8ccceef442eb2cd5b052cba3562d2b1b1a3a4ba6
9c47b2af8b8c5f3c25f237dcc375b41835904f7cd99221c7489fb3563c34c9ab
211b7b7a4c4a07b9c65fae361570dbb94666e26f0cc0fa0b32df4b09fcee6de2
fd61a5cd1a83f68b75d47c8b6041f8640e47510925caee8176d5d81afac29134
84f822d9cf575aeea867e9b73f88ad4d9244293e52208644e12ff2cf13b6b537
855cf3a6422b0bf680d505720fd07c396508f67518670b493dba902c3c2e5dfa
4b4c6b36938c3de0623feb92c0e1cb399d2dc338d2095b8ba84e862ef6d11772
5dd162ab66f0c819ee73868c26ecd82408422e2b6366805631eab95ae32516f3
6e2991e02d3cf17d77173d50cdaa766661a89721c3cc4050fba98bea0dbdb1a9
1e8ed6e8d0b6fc47d8176c874ed40fb09644c058042f34d987878fa644f493cc
647e379517fed71682423b0192da453ec1d61a633c154fdd55bab762bcc404f3
ebd4f45cbb272bcc4954cf1bd0a5b8802a6e501688f2a1abdb6143ba616aea82
edc49bf7ec508becb088d5082c78d360f1a7cad520f6de6d8b93759b67aac305
7482f8c86b63ce53edcb62fc2ff2dd8e584e2164451ae0c6f2b1f4d6d0cb6d9c
2fbd3d2362acd1c8f0963b48d01f94c7a07aeac52d23415d0498c8c9e23554db
154e3a12404202fd25e29e754ff78703d4edd7da73cb4c283c9910fd526d47db
fc5f7a21d953c394968647df6a37e1f61db04968ad1aca65ad8f261b363fa842
a1d5b7d69d85b1be31d9e1cb0686094cc7b1213079b2a66ace01be4bfe3fb7c3
4b0203492a95257707a86992e84b5085ce9e11810a26920dbb085005081e32d3
a05805bcec72fb76b997c456e0fd6c4b219fdc51cad70d4a58c16b0b0e2d9ba1
4e953ea82b0406a5b95e31554628ad6821b1d91e9ada0d26179977f227cf01ad
6272ed2a9b69509ac16162158729762d30f9ca06146a1828ae17afedd5c243ef
440504899b7af6f352cfaad6cdef1642c66927ecce0cf2f7e65d563a78be1b29
Carp Downloader samples (binaries and documents)
9a2491d803407b8696d6b797f8b90d728a8db3583bf4c2977cbeef8be0eb7249
7220e659d59491db50661c54762b49bf6976acbeb723b5d59abde48301c86228
c2d944a939bdc810d603149c0685f0bcb55a84d1f3a6ea33e9debe893fd0a8dd
d562f01384b1d215758227fb2c165ed633fe9997096613fed8ce3bdf8963e4fd
fdee357557a69d3dfa629d0cbd585d9c5dadc526dfb424af56c8edcc7a67d556
0716f3f9cb0dead0c1f156a07adfeb3e0d72e4ea4af7b67238fae3e1ae670f90
2016766acaeb1b89415fb6ef03f6ee815b8fe76b8955a6a41d2bbb28dfa74c28
d7996ac876fa0ece281e49e7955dfbbf4ef1239b1ee63a0e21d6c4ed4b7c6559
96067fc9b137ceecab2ff29ac56ff6897a7c73657ace7c40d70b7c1ebaaccf39
ea581e8e625a3748da9663414182d1b99f9c5ddb0b9db2fbf1059a28c69cc10c
a2dfe3a5a1e999af7f1920d28e05d8b0ce66c6e8b2947177878862ce1f870b17
5665527ce54ed1a79ddb8e3c10499ac0b7af5c79a8cf5a37448baccbf6dba09f
b4632dcf0b23467970ee7e0844e7c8a931dc3a0f549c0aa5e40e41c1b5b31fdc
6ecd376cdc182bf157e59d500da6092891e6cd9a61305214e462d6e990e6e834
0fabc65c316e8d84493d07cd39bfdd59481af9f9a7ebc9103693f1788438a438
a52ba498d304906d6c060e8c56ad7db50e1af0a781616c0aa35447c50c28bae9
5025aa0fc6d4ac6daa2d9a6452263dcc20d6906149fc0995d458ed38e7e57b61
1181f97071d8f96f9cdfb0f39b697204413cc0a715aa4935fe8964209289b331
d5d885734969641f43c64edf9788837df0d3452413a7ef835f8910d56c60c91c
0438becfd66d728778f47d734d2f0bc4d1462d945cf4b6dde9fbf627eb0bb02d
84e705341a48c8c6552a7d3dd97b7cd968d2a9bc281a70c287df70813f5dca52
ae1a6c4f917772100e3a5dc1fab7de4a277876a6e626da114baf8179b13b0031
e49e61da52430011f1a22084a601cc08005865fe9a76abf503a4a9d2e11a5450
192b204dbc702d3762c953544975b61db8347a7739c6d8884bb4594bd816bf91
571b58ba655463705f45d2541f0fde049c83389a69552f98e41ece734a59f8d4
10f53502922bf837900935892fb1da28fc712848471bf4afcdd08440d3bd037f
8bea55d2e35a2281ed71a59f1feb4c1cf6af1c053a94781c033a94d8e4c853e5
057965e8b6638f0264d89872e80366b23255f1a0a30fd4efb7884c71b4104235
EVILNUM samples
97c97ad2baef37eea023549131c192f441aa7976747166cd31095e7dad17948c
bee6c5a506d6fb2cc129443c74b7676fbb9a79b53b92b2cac4c7fb8209592714
7f0c5e2850d10d4bf129e0d290010bedff44a0f506d92de79ef6d69fd78487e3
508e25a0e729824f06f4960b635600acf3cab87ebb87854d1989ff0ba2f03e78
997de4372efd576cdb55188a06e4699660a29c37e285e23cdd8a1a9585e6e789
e5e172cd93e97480a9982f821c8f1bdf9756803a3fb8a1a7a39e262cda192cb6
8db0118d4bbc10efd0fd6733d987ddeee7afc6c3ebe4ee1157ae9243aba362d9
Cardinal RAT Infrastructure (samples observed from mid 2017 onwards only)
s.dropinbox[.]host
secure.dropinbox[.]pw
s.spotmacro[.]online
secure.spotoption[.]pw
190.10.8[.]238
affiliatecollective[.]club
EVILNUM Infrastructure
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/venomisherenow/wearevenom/master/README.md
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/idontwantcofee/ihavepoop/master/README.md
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/yoshimaster8/whatcha/master/readne
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/grobagala/pizza/master/readne
hxxps://gitlab[.]com/githubuser/testing/commits/master
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/sarutubi/Luckyluke/master/README.md
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/hititdolly/justcallmeangel/master/README.md
hxxps://www.codeplex[.]com/site/users/view/saidjaosdjo
hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/iuasbduias/auhidshas/master/README.md
hxxps://www.digitalpoint[.]com/members/bitbox123.922831/
139.28.37[.]0
127.194.87[.]192 # likely attacker testing
127.194.73[.]243 # likely attacker testing
wikipeldia[.]org
185.247.211[.]198
185.20.187[.]4
193.22.96[.]98
193.22.98[.]182
193.22.99[.]168










 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42