Threat Assessment: Dharma Ransomware
Executive Summary
Dharma, aka CrySIS or Wadhrama, is a ransomware family first identified publicly in 2016. Dharma targets Windows hosts at organizations in several ways, including malicious attachments in phishing emails. Dharma has served as the code base for later ransomware families, such as Phobos, which was discovered in 2019. Additionally, the actors behind Dharma have leveraged disguised installers that appear to be legitimate software installers, such as antivirus software.
In addition to Dharma being distributed in spam emails and malicious installers, Dharma is also distributed to victims via exposed, vulnerable or brute-forced Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) services.
Dharma Ransomware Overview

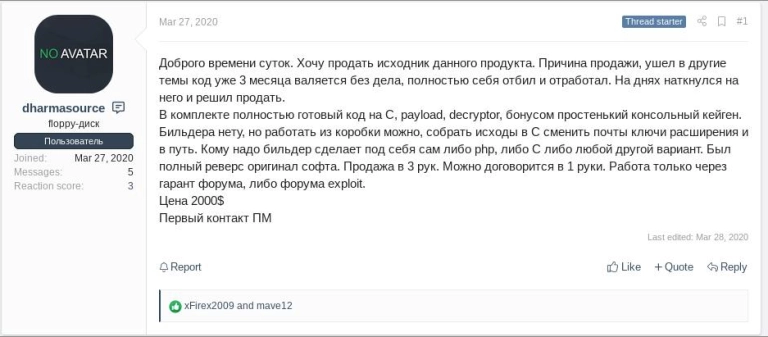
Dharma is routinely distributed or sold as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) offering on underground forums and social networks.
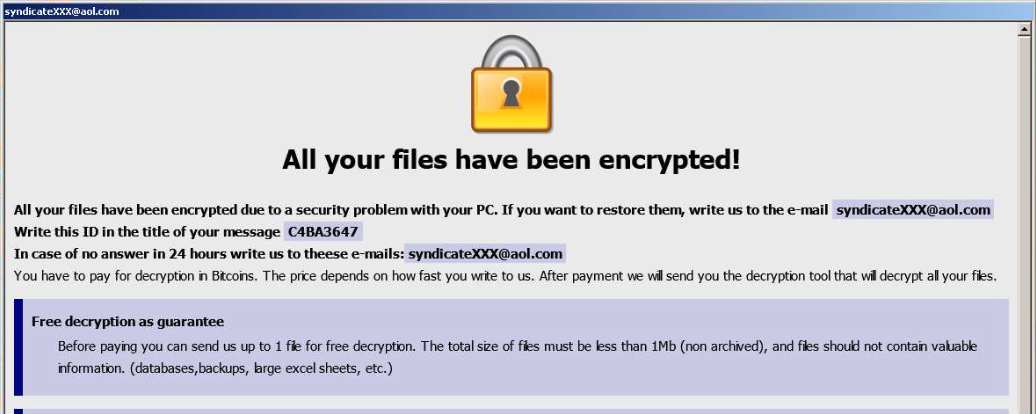
After Dharma completes encryption of victim files, Dharma drops a ransom note on the desktop that contains an email address to contact with a desired ransom amount. Average ransom amount paid in 2020 was $7,801, with some variance in ransoms demanded occurring based on the target’s organizational size.
Upon encryption of infected files, the following file extensions have been observed appended to the file name:
.crysis, .dharma, wallet, .java, .adobe, .viper1, .write, .bip, .zzzzz, .viper2, .arrow, .gif, .xtbl, .onion, .bip, .cezar, .combo, .cesar, .cmb, .AUF, .arena, .brrr, .btc, .cobra, .gamma, .heets, .java, .monro, .USA, .bkp, .xwx, .btc, .best, .bgtx, .boost, .heets, .waifu, .qwe, .gamma, .ETH, .bet, ta, .air, .vanss, . 888, .FUNNY, .amber, .gdb, .frend, .like, .KARLS, .xxxxx, .aqva, .lock, .korea, .plomb, .tron, .NWA, .AUDIT, .com, .cccmn, .azero, .Bear, .bk666, .fire, .stun, .myjob, .ms13, .war, .carcn, .risk, .btix, .bkpx, .he, .ets, .santa, .gate, .bizer, .LOVE, .LDPR, .MERS, .bat, .qbix, .aa1, and .wal
Like many ransomware families found in the wild today, Dharma shares several actor and code similarities with other families (i.e. Phobos).
Both families share the same ransom note post-infection. Additionally, initial correspondence from the victim to both actors is the same. There are, however, several code differences between Dharma and Phobos, namely in the file structure.
Palo Alto Networks observed victims in the insurance, transportation and logistics, high tech, healthcare and government sectors, mainly focused on small and mid-sized businesses. Victims were located in the U.S., Italy, Japan and India.
More information on Dharma victimology can be found in the 2021 Unit 42 Ransomware Threat Report.
Courses of Action
This section documents relevant tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) used with Dharma and maps them directly to Palo Alto Networks product(s) and service(s). It also further instructs customers on how to ensure their devices are configured correctly.
| Product / Service | Courses of Action |
| Defense Evasion, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Discovery | |
| Mshta [T1218.005], Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder [T1547.001], Process Injection [T1055], DLL Search Order Hijacking [T1574.001], Software Packing [T1027.002], Masquerading [T1036], Modify Registry [T1112], Bypass User Access Control [T1548.002], Process Discovery [T1057], Process Hollowing [T1055.012] | |
| NGFW | Ensure application security policies exist when allowing traffic from an untrusted zone to a more trusted zone |
| Ensure 'Service setting of ANY' in a security policy allowing traffic does not exist | |
| Ensure 'Security Policy' denying any/all traffic to/from IP addresses on Trusted Threat Intelligence Sources Exists | |
| DNS Security | Enable DNS Security in Anti-Spyware profile |
| URL Filtering | Ensure that URL Filtering is used |
| Ensure that URL Filtering uses the action of ‘block’ or ‘override’ on the <enterprise approved value> URL categories | |
| Ensure that access to every URL is logged | |
| Ensure all HTTP Header Logging options are enabled | |
| Ensure secure URL filtering is enabled for all security policies allowing traffic to the internet | |
| Cortex XDR Prevent | Enable Anti-Malware Protection |
| Cortex XSOAR | Deploy XSOAR Playbook - Endpoint Malware Investigation |
| Threat Prevention | Ensure that antivirus profiles are set to block on all decoders except 'imap' and 'pop3' |
| Ensure a secure antivirus profile is applied to all relevant security policies | |
| WildFire | Ensure that WildFire file size upload limits are maximized |
| Ensure forwarding is enabled for all applications and file types in WildFire file blocking profiles | |
| Ensure a WildFire Analysis profile is enabled for all security policies | |
| Ensure forwarding of decrypted content to WildFire is enabled | |
| Ensure all WildFire session information settings are enabled | |
| Ensure alerts are enabled for malicious files detected by WildFire | |
| Ensure 'WildFire Update Schedule' is set to download and install updates every minute | |
| Cortex XDR Prevent | Configure Behavioral Threat Protection under the Malware Security Profile |
| Enable Anti-Exploit Protection | |
| Lateral Movement | |
| Replication Through Removable Media [T1091] | |
| Cortex XDR Prevent | Enable Device Control |
| Impact | |
| Inhibit System Recovery [T1490], Data Encrypted for Impact [T1486] | |
| Cortex XSOAR | Deploy XSOAR Playbook - Palo Alto Networks Endpoint Malware Investigation |
| Deploy XSOAR Playbook - Ransomware Manual for incident response. | |
Table 1. Courses of Action for Dharma ransomware.
†These capabilities are part of the NGFW security subscriptions service.
Conclusion
Similar to many ransomware families Unit 42 tracks daily, Dharma shares several actor and code similarities with the Phobos ransomware family. Dharma is particularly loathsome ransomware because many organizations across the globe rely on its initial infection vector (RDP). The impact a group of determined attackers can have against organizations – and the actors’ code and infrastructure reuse – can be devastating.
Palo Alto Networks detects and prevents Dharma in the following ways:
- WildFire: All known samples are identified as malware.
- Cortex XDR with:
- Indicators for Dharma.
- Anti-Ransomware Module to detect Dharma encryption behaviors.
- Local Analysis detection to detect Dharma binaries.
- Next-Generation Firewalls: DNS Signatures detect the known command and control (C2) domains, which are also categorized as malware in URL Filtering.
- AutoFocus: Tracking related activity using the Dharma tag.
Additionally, Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) associated with Dharma are available on GitHub, and have been published to the Unit 42 TAXII feed.
Additional Resources
- Color by numbers: inside a Dharma ransomware-as-a-service attack
- A deep dive into Phobos ransomware
- NJCCIC Threat Profile
Continue Reading: GandCrab & REvil











 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42