This post is also available in: 日本語 (Japanese)
Overview
The Unit 42 threat intelligence team recently shared its latest findings at Microsoft’s invitation-only security conference, BlueHat Seattle 2019, on three new Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) vulnerability exploitation methods for Pool Feng Shui techniques. Pool Feng Shui is an advanced vulnerability exploitation technique that manipulates the kernel pool layout and state finely to facilitate arbitrary code execution.
The report, titled “Pool Fengshui in Windows RDP Vulnerability Exploitation,” is authored by Tao Yan and Jin Chen, shared three new Windows RDP vulnerability exploitation methods for Pool Feng Shui techniques. Yan not only showed how Bitmap Cache PDU, Refresh Rect PDU and RDPDR Client Name Request PDU can be used for Pool Feng Shui in the Windows RDP vulnerability exploitation, but also shared ideas about how to find Pool Feng Shui friendly protocol data unit (PDUs) from massive RDP documents and Windows RDP modules. These new techniques were demonstrated live to exploit the wormable BlueKeep Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708) and can also be used in other Windows RDP vulnerabilities.
BlueHat Seattle 2019
Presented in a closed-door session by Yan, attendees in the research community dubbed this talk the “Best Talk of BlueHat.” Sharing this research arms defenders with knowledge about how Windows RDP vulnerabilities can be exploited and enables them to develop capable prevention techniques. The researchers showed that mitigating the exploitation techniques can not only decrease the possibility of BlueKeep to be exploited but also decrease the possibility of other Windows RDP vulnerabilities to be exploited successfully. This is part of Palo Alto Networks’ continued effort to disarm the advanced adversary.
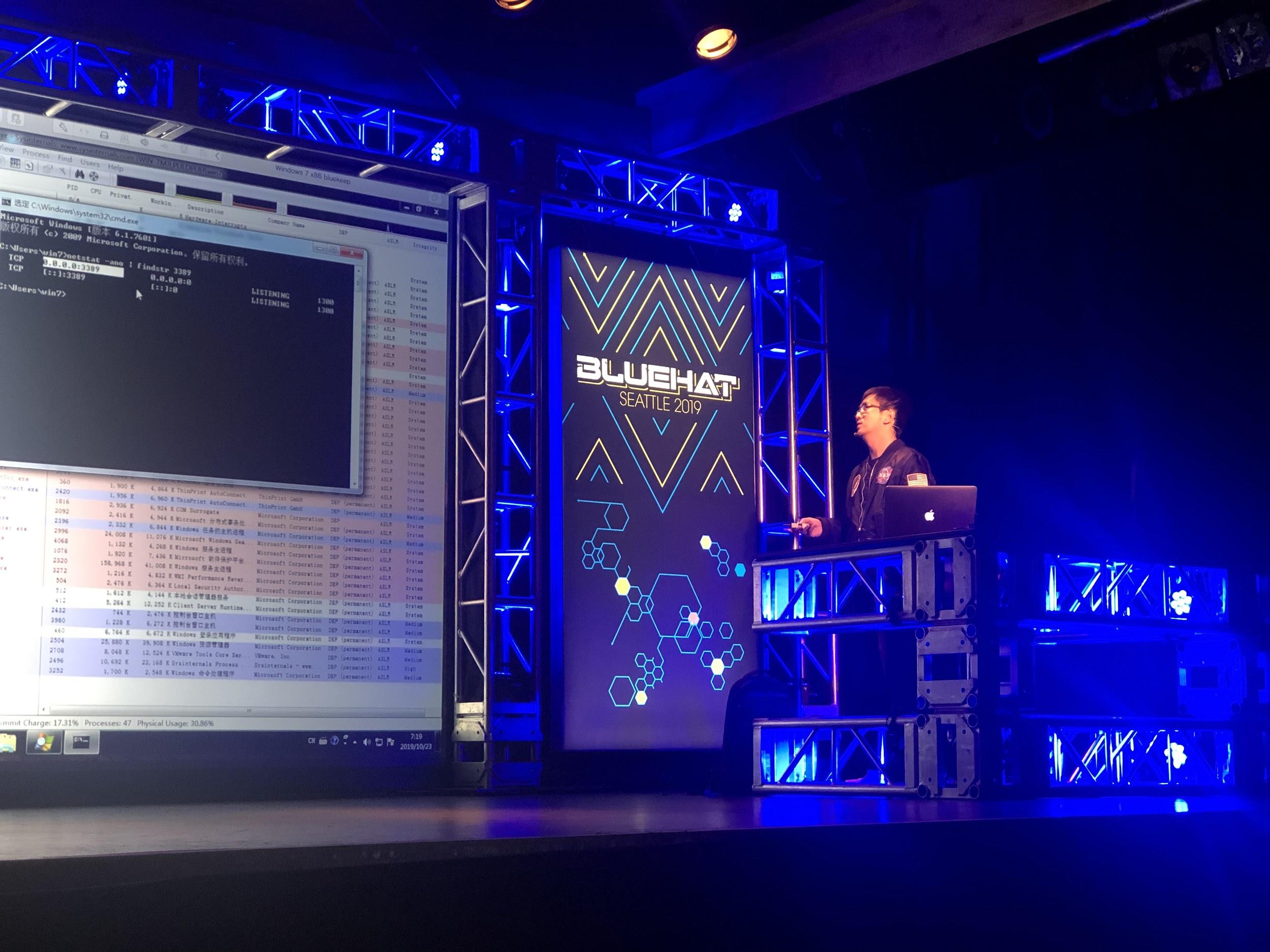
Figure 1. Tao Yan Demos the Windows RDP Vulnerability BlueKeep Exploitation
Conclusion
Weaponized exploits for these vulnerabilities are prevented by Palo Alto Networks’ Traps multi-layered exploit prevention capabilities. Threat prevention capabilities, such as vulnerability protection with IPS and WildFire, provide our customers with comprehensive protection and automatic updates against previously unknown threats.











 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42