Introduction
Parts 1, 2 and 3 of our Cybercrime Underground the cybercrime series discussed some of the concepts and definitions around cybercrime, and how cybercriminals collaborate in cybercrime forums in buying and selling malicious tools and services. This latest report in our cybercrime series will provide a glimpse of the darknet markets where cybercriminals buy and sell data which have likely been stolen directly by compromising victim computer systems or by the result of a large database compromise. This blog focuses on explaining what darknet markets are, common payment model used, the type of digital data being bought and sold in the darknet markets and their typical costs. The objective of this blog is not to provide an exhaustive list of all the products and services being sold in the darknet markets but to shed light on how cybercriminals are utilizing the darknet markets to trade with impunity. It is important to understand the impact to the growing number of cybercrime campaigns and how the stolen data is monetized by the cybercriminals due to the demand in specific PII data in the darknet markets.
Many articles and research published by the information security industry discuss how cyber attacks can be broken down in phases which is widely known as the cyber kill-chain model. Darknet markets also play two important roles in the overall attack kill-chain. First these markets allow cybercriminals to purchase tools which are then utilized in specific stages of the kill-chain. For example: Malware creation and exploit tools which are sold in the darknet markets aid cybercriminals during the 'weaponization' and 'exploitation' phase of the kill-chain model respectively. The last phase of the kill-chain model 'Actions on Objectives', specify the objective or goal of an adversary. Second, darknet markets allow cybercriminals to achieve their goal of making monetary profit by selling the data which may have likely been stolen from victim computer systems. It is also worth noting that not all digital data being sold in the darknet markets are gained from the result of successful cyber attacks. Insider data theft can end up in a darknet market as well. Insiders with the knowledge and know-how on sensitive information can aid in creating fake identification products which look authentic. For example a former Australian police officer was arrested in November 2016, for creating and selling fake police IDs, security and maritime passes in a darknet market.
The darknet markets today have increased in numbers as well as the number of users- one of the primary reasons has been the anonymity the darknets provide to the users to perform their illicit and illegal trades as well as the decentralized architecture provided by the Tor network which makes it increasingly difficult for law-enforcements to take actions against darknet markets.
What are Darknet Markets?
Darknet markets are websites which are hosted on the deep-web and can be accessed typically using the Tor network. The products and services which are bought and sold in the darknet markets can range from stolen credit-cards, personal information & ID scans, personal credit reports, operating accounts of online payment systems, email accounts with stolen credentials, counterfeit items, malware & exploit kits, drugs and also weapons, among other illegal products.
Access to Darknet Markets:
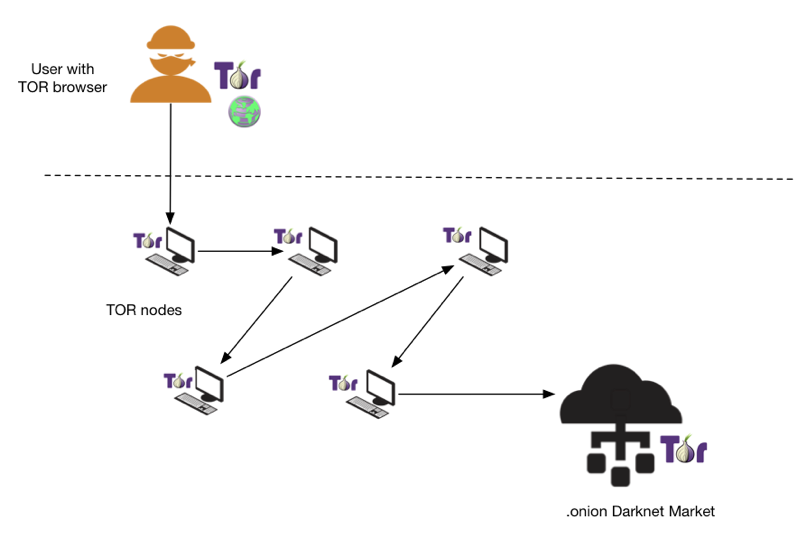
Darknet markets are hidden websites which cannot be accessible using regular browsers or search engines as they do not have an actual DNS name. Most darknet markets have a .onion TLD suffix which states that it is a hidden service and can only be reachable by the TOR network. A .onion site consists of 16 alphanumeric characters followed by a .onion TLD. The 16 characters may include letter from 'a to z' and numeric numbers from '1 to 7'. Below is a syntax of a .onion hidden service.
SYNTAX: [digest].onion
The digest is the base32 encoded value of the first eighty bits of a SHA1 hash of the identity key for a hidden service. Once Tor sees an address in this format it tries to connect to the specified hidden service. Many darknet market users also use a VPN network to add an additional layer of privacy to hide their source.
Figure 1 High-level depiction on how darknet markets are accessed using Tor
Payment Model:
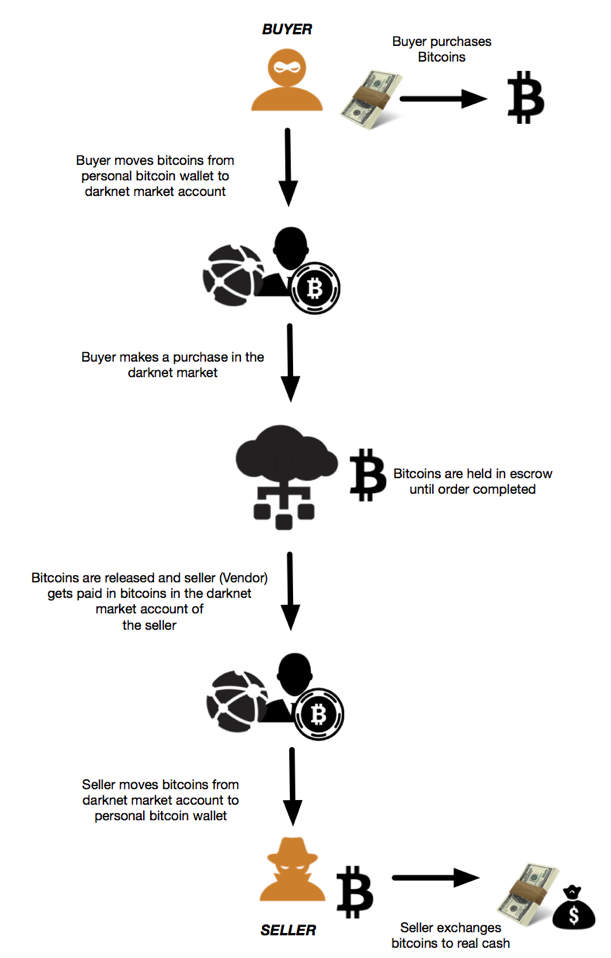
The payment process in the darknet markets has followed the process which was used by the “Silk Road”, one of the first and best known darknet markets. Purchases in the darknet markets are typically made using virtual currencies like Bitcoin. An individual who wants to buy a product in the darknet market needs to credit his/her darknet market account with Bitcoins to make purchases in the darknet market. The buyer purchases and moves Bitcoins to the darknet user account used by the buyer and makes the desired purchase. Once the buyer has initiated the purchase, the respective cost of the purchase in Bitcoins from the buyer's account are held in the darknet market's escrow until the order has been completed. Once the purchase order has been completed, the Bitcoins are released to the Seller (Vendor). The figure below shows a flowchart of the payment model being used in darknet markets.
Figure 2 Payment model of Darknet Markets
Common Types of Data Bought & Sold:
Darknet markets provide many types of illegal products to be sold. This blog will not cover all the product types being available in the darknets but cover some of the most common types of information/ services which are transacted by cybercriminals in the darknet markets. Some of the types which we will discuss in this blog are:
- Credit Cards/ CVV numbers
- Credit Score Reports
- Passport Scans
- Driving license Scans
- Document scan templates
- Compromised account credentials
- Malware/ Exploit kit services
Credit Cards:
It is not a surprise to see ‘credit cards’ being sold in the darknet markets as they are further used to commit fraud and are also used by cybercriminals to finance their requirements and make profit. There are multiple ways in which credit cards are stolen – some of which are phishing scams, ATM skimmers and also by people in the industry who have access to customer credit card information. Credit card fraud has been costing the financial industry billions of dollars and due to the high number of credit card frauds, the financial industry may find it overwhelming to investigate every fraud incident and may only tend to focus on cases where the cost of the fraud is very high. The cybercriminals / fraudsters are well aware of this challenge and try to perform their fraud activities by transacting small number of transactions on each card to avoid being detected by anti-fraud systems. The below snap shot was taken from a credit card sales ad at a darknet market where a seller also provides advice on making less amount transactions per card to avoid getting detected.
Figure 3 Seller advises buyers to make low transactions to avoid detection
The typical cost of credit cards being sold in the darknet markets can range from USD $1 to $25 for each card. The cost is higher if there is a confirmed high balance or if it is a premium card (platinum, business, corporate, gold). Some of the costs can be much higher if they come in a bundle and may also include how-to tutorials on making the most out of the credit cards to conduct fraud.
Figure 4 below shows some of the most recent credit card sales listings on a darknet market.
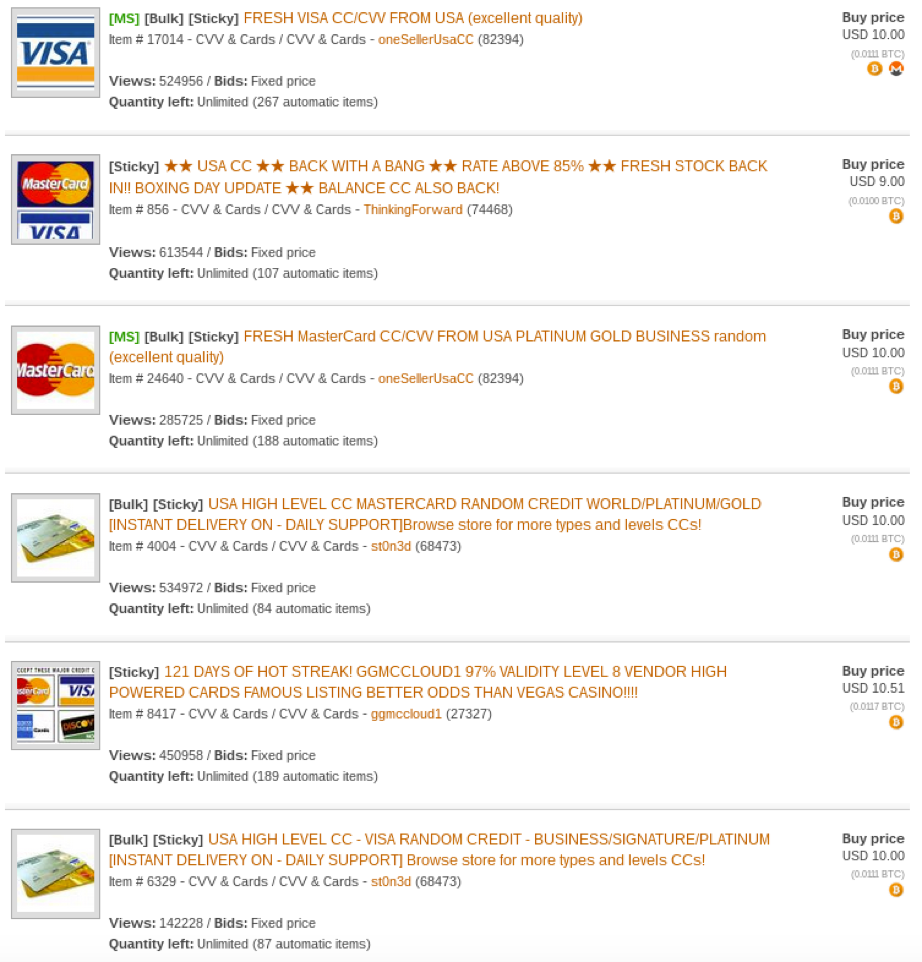 Figure 4 Credit Card listings on a darknet market
Figure 4 Credit Card listings on a darknet market
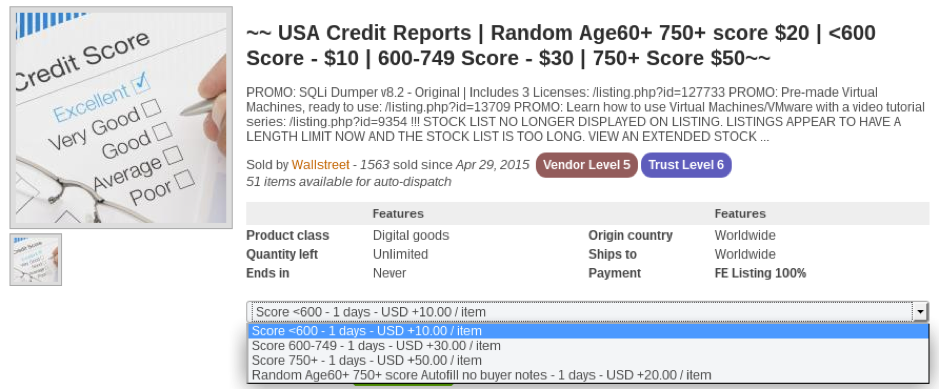
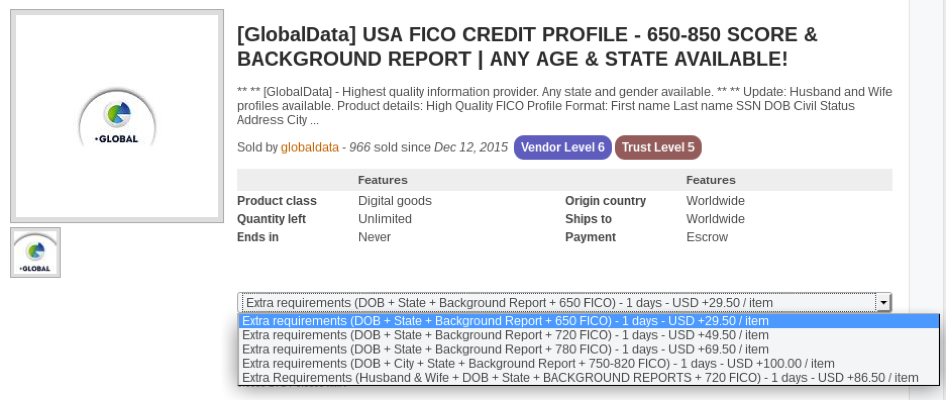
Credit Score:
Stolen identities are in big demand in darknet markets as they allow cybercriminals to conduct fraud using real identities of individuals who could have been victims to phishing/malware attacks or organizations holding PII data of their customers getting breached. Credit Score reports are one of the most highly traded PII (personally identifiable information) in the darknet markets. A credit score report is an analysis report of the credit worthiness of an individual and the credit score depends on the credit files of a person. Financial organizations use credit score reports to assess a client’s credit history which is used to approve loans. Credit reports are not only used by financial organizations but many others like governments, insurance, and many other organizations which require a credit history to process a request. The price of the credit score lists depends on the score of the report, with the higher score reports going for a higher price. Figure 5 and 6 below shows two examples of credit report listings which are being sold on a darknet market. A credit score of 750+ costs USD $50 in one of the listing and another listing shows a score between 720 and 820 would range between USD $ 49.50 to $100.
Figure 5 Example credit report listing on a darknet market
Figure 6 Example credit report listing at a darknet market
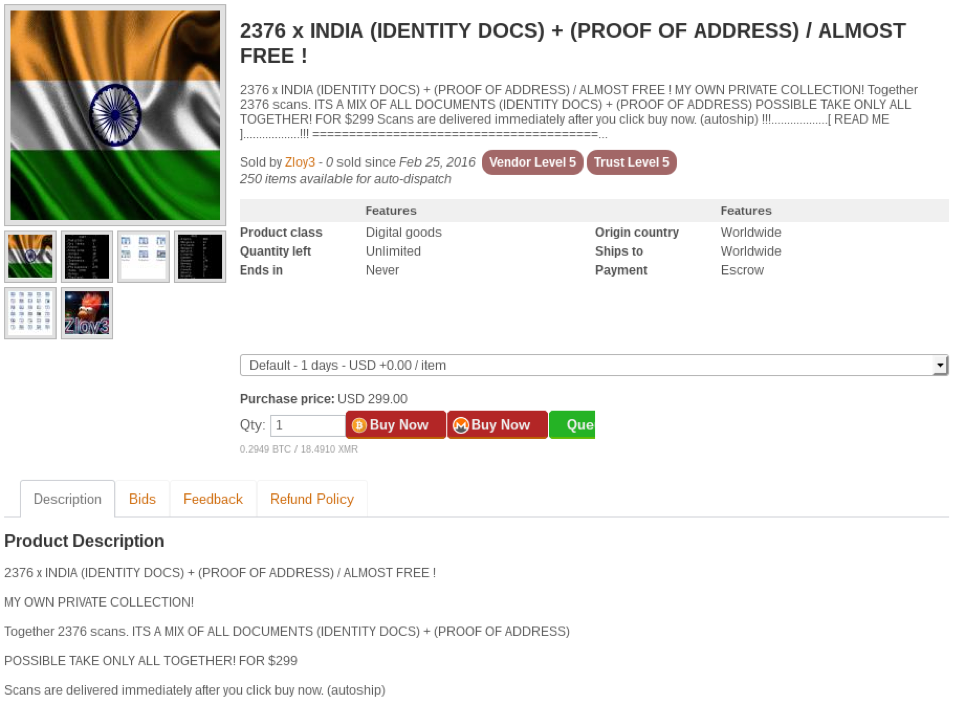
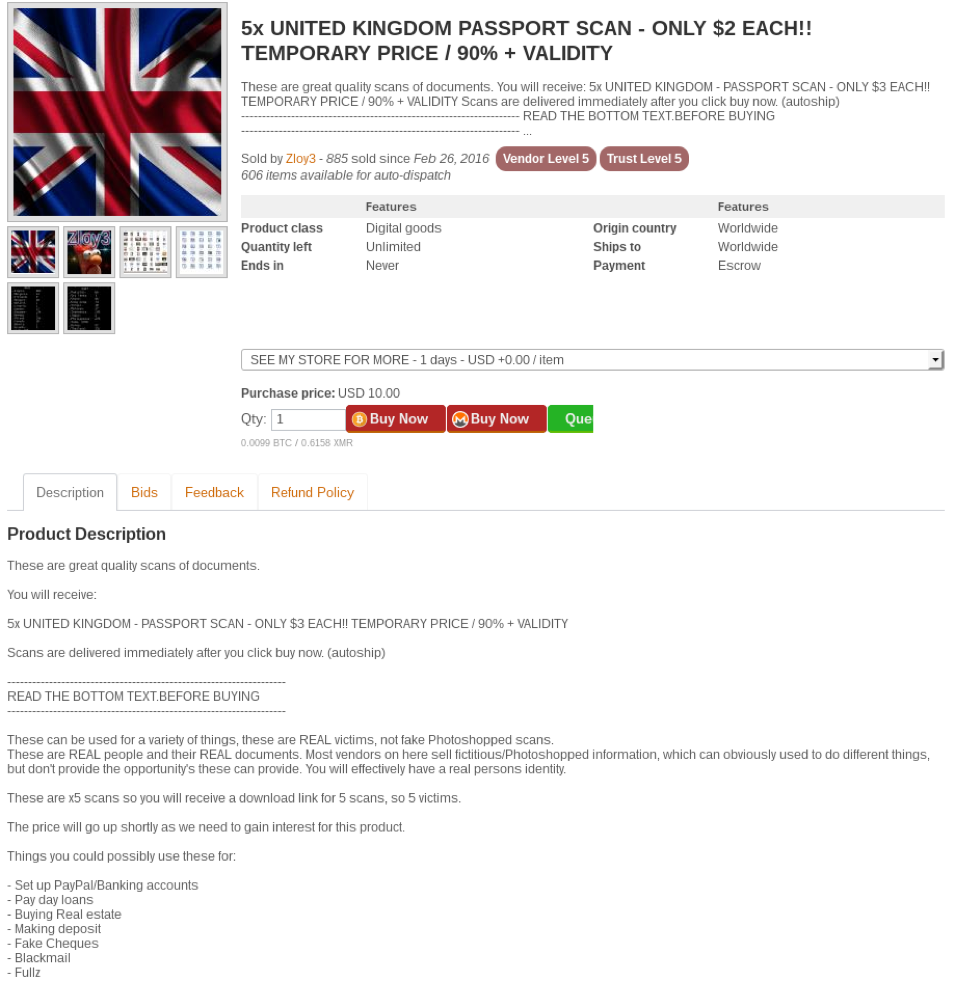
Passport / Driving License Scans:
Identity documents like passport and driving license scans are also in high demand as they can be used to commit fraud which can range from opening bank accounts, PayPal accounts, purchasing real estate, and perform any other transactions which may require a scanned copy of a passport or a driver’s license for verification. Many developed nations have a robust digital architecture with public services being available online where such scanned copies can be used to process and transact services by using real identities which are being sold in the darknet markets, further fuelling the opportunities to commit fraud. Even developing nations are not immune to these threats- Nations like India are investing heavily in transforming its digital architecture to provide public services electronically and encourage citizens to use the internet and the online services being provided. Given Personal Identifiable Information (PII) data are used in many such services, these type of information are in demand in the darknet markets as they can be used to conduct multiple types of fraud.
Figure 7 Listings showing passport and ID scans of India and UK being sold on a darknet market
Document Scan Templates:
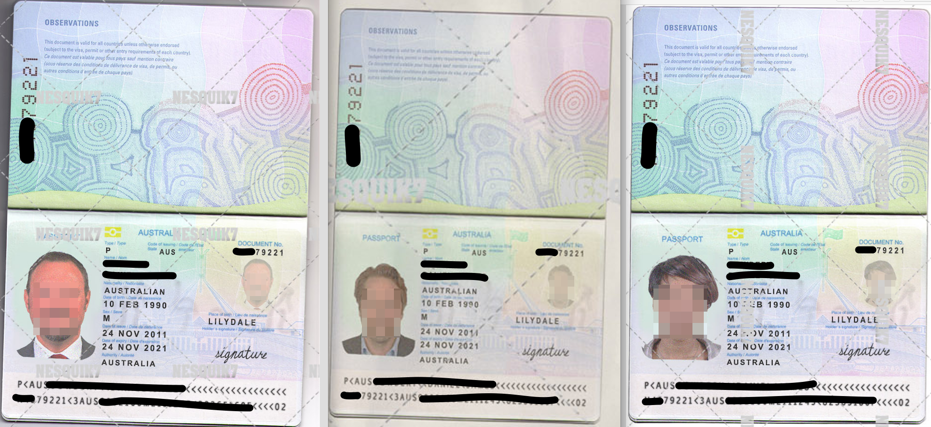
Another type of listing which is quite regular in the darknet markets include but are not limited to templates of passports, driving licenses, SSNs, bank statements, utility bills, credit cards, tax statements and invoice receipts of different vendors. Figure 8 is an example of a sample of an Australian passport template which has the same passport ID details but has different photos of individuals. The seller of the below template also shares that any details in the passport including the photograph can be changed and it would still look legitimate. The seller provides full editable versions of the template in .psd format which is an Adobe Photoshop document format. The seller also provides download links to cracked versions of Adobe Photoshop so the buyers can use the .psd files without needing to buy a licensed copy of the software. Each .psd template sold can cost between USD $20 to $100. However, many listings have these templates being sold in bundles as well- For example a list of 9 templates for Canadian documents consisting of passport scans, bank statements, invoice documents and utility bills is selling on a discounted price of USD $387 where the original price would have exceeded $500 if bought separately.
Figure 8 Scanned templates of Australian passports being listed at a darknet market
Compromised Account Credentials:
Credentials of many online services which include banking, telco, social media networks and many more are being listen in the darknet markets. Figure 9 shows some of the listings of compromised accounts being sold at a darknet market.
Figure 9 Compromised credentials being sold at a darknet market.
Malware / Exploit Kit Services:
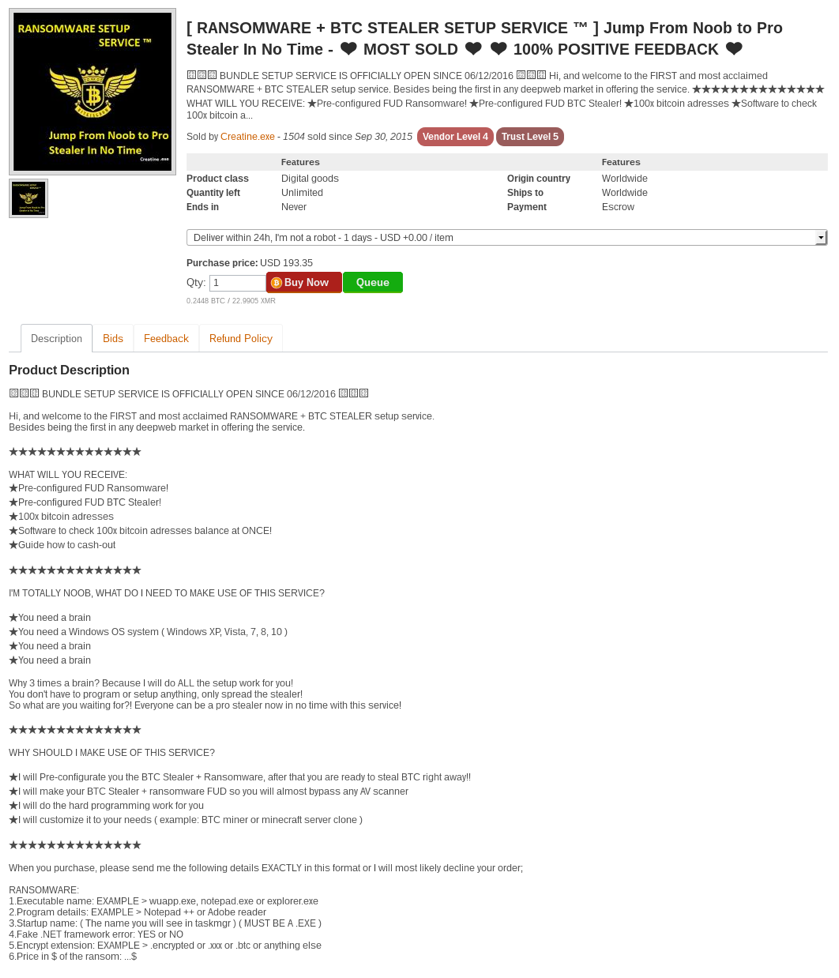
There are many types of malicious tools and services being sold in the darknet markets, some of which we have already shared in part 2 of our cybercrime underground series. Figure 10 below shows a listing on a darknet market for a Ransomware and BTC stealer setup service where a seller provides the tools and also configures it for the buyer.
Figure 10 Ransomware service being listed on a darknet market
Impact:
The global cost of cybercrime has been on an alarming rise with the estimated loss to be in billions of dollars, with some reports indicating that the overall loss could be in trillions. A large portion of this cost can be attributed to the fraud conducted due to stolen PII data, some of which we have covered in this blog. For example- In Asia, Australia has been impacted the most due to identity crimes with an estimated loss of AUD $2.2 billion annually. The Australian Federal Police also mention that identity crime has been a key enabler to 'organised crime' which in turn has been costing Australia AUD $15 billion dollars annually. This really shows the vast impact nations and organizations are facing due to the identity and PII information being stolen, bought, and sold in the darknet markets.
Conclusion:
Darknet markets have allowed cybercriminals, fraudsters and criminals who trade in weapons, drugs and illegal products to trade without much concern of getting caught due to the anonymity provided by the deep-web. Though it may be difficult to identify the perpetrators who are managing or using the darknet markets for their profit, global law-enforcement agencies are continuously working to bring the criminals behind the darknet markets to justice and the number of successful cases has been growing where many criminals behind the darknet markets have been arrested. Large percentage of internet and online service users are often unaware of the threats in the digital world and tend to not follow common online safety measures to secure their personal information or their systems, which eventually result in their personal data being stolen and traded in darknet markets, where the information are further used to commit fraud. It is imperative to have an understanding on how these criminals operate and the type of information being traded to better secure ourselves.
Organisations should follow industry standards on securing data and implement security technologies to prevent cyber attacks and reduce the risk of data being stolen and traded in the darknet markets. Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation security platform provides a holistic solution to protect the digital way of life by safely enabling applications and preventing known and unknown threats across the network, cloud and endpoints. For more information on the next-generation security platform visit here.
References:
- http://blog.paloaltonetworks.com/2016/08/unit42-exploring-the-cybercrime-underground-part-1-an-introduction/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silk_Road_(marketplace)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Darknet_market#/media/File:Marketlifetimes.png
- https://gitweb.torproject.org/torspec.git/tree/address-spec.txt
- https://svn.torproject.org/svn/projects/design-paper/tor-design.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Credit_score
- http://digitalindia.gov.in/content/about-programme
- https://www.deepdotweb.com/tag/arrested/
- https://www.ag.gov.au/RightsAndProtections/IdentitySecurity/Pages/Trends-in-Identity-Crime.aspx
- http://cybersecurityventures.com/hackerpocalypse-cybercrime-report-2016/
- https://www.juniperresearch.com/press/press-releases/cybercrime-cost-businesses-over-2trillion
- https://www.afp.gov.au/what-we-do/crime-types/fraud/identity-crime
- http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/mf/4528.0/
- https://www.ag.gov.au/RightsAndProtections/IdentitySecurity/Documents/Identity-crime-and-misuse-in-Australia-2016.pdf
- http://www.lockheedmartin.com/content/dam/lockheed/data/corporate/documents/LM-White-Paper-Intel-Driven-Defense.pdf
- https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/products/designing-for-prevention/security-platform














 Get updates from Unit 42
Get updates from Unit 42